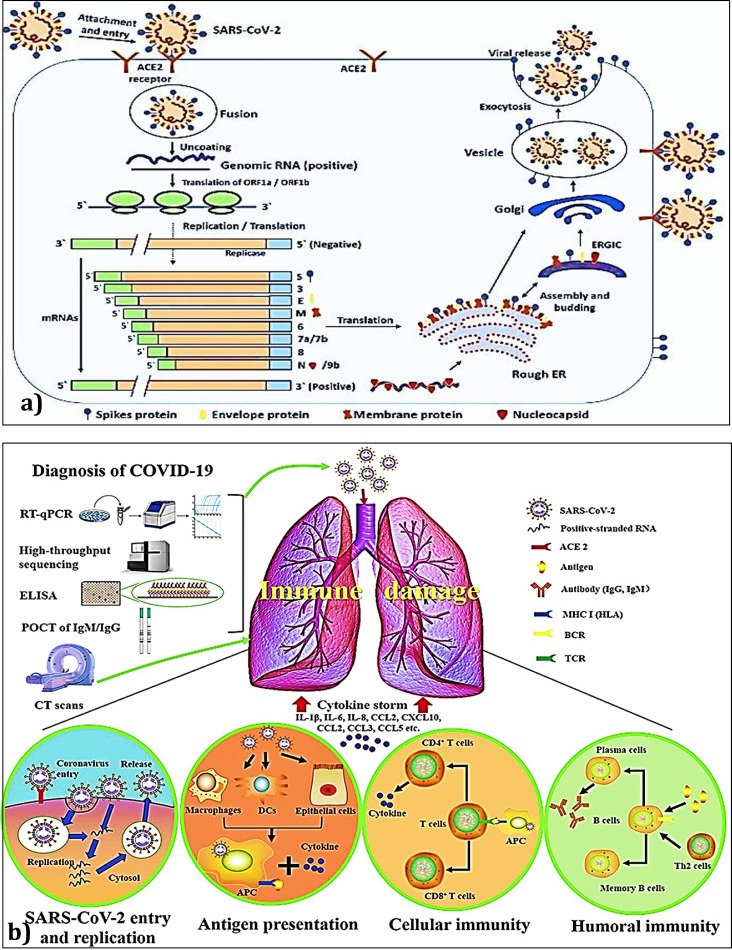
Fig. 7.
Propagation of CoV-19 in host cells via S protein that binds ACE2.
a)After S binds to ACE2, the conformation change in the S protein to cleave it into S1 and S2 proteins that facilitates viral envelope fusion with the cell membrane through the endosomal pathway. Then CoV-19 releases RNA into the host cell and its RNA is translated into viral replicase polyproteins pp1a and 1ab, which are then cleaved into small products by viral proteinases. The polymerase produces a series of sub-genomic mRNAs by discontinuous transcription and at the end, translated into relevant viral proteins. Viral proteins and genome RNA are subsequently assembled into virions in the ER and Golgi and then transported via vesicles and released out of the cell. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERGIC, ER–Golgi intermediate compartment (reproduced from Shereen et al. (2020) under a Creative Commons license). b) Different stages of growth and propagation of COVID-19 in human lungs (reproduced from Li et al. (2020b) under a creative commons license).