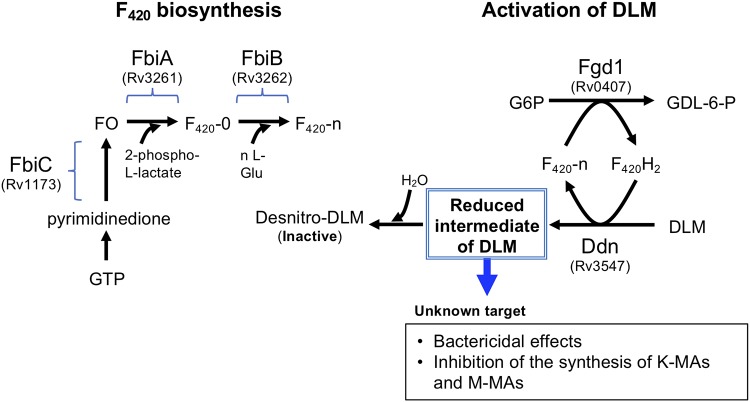
FIG 1.
Biosynthesis of coenzyme F420 and F420H2-dependent reduction of DLM in M. tuberculosis. The 7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin (FO) is synthesized from pyrimidinedione by a series of reactions catalyzed by enzymes, including FbiC (Rv1173) (5). FbiA (Rv3261) transfers a 2-phospho-l-lactate moiety to FO, resulting in the synthesis of F420 with no poly-γ-glutamate tail (F420-0) (6). FbiB (Rv3262, γ-glutamyl ligase) catalyzes the addition of l-Glu to F420-0, resulting in the synthesis of F420-n (6, 7). Coupled with oxidation of G6P and reduction of F420 by Fgd1, DLM is reduced by F420H2-dependent Ddn (Rv3547) (2–4). The reduced intermediate of DLM is deduced to attack an unknown target. A major part of the reduced intermediate is further converted in mycobacteria to desnitro-DLM (inactive form) by H2O quenching.