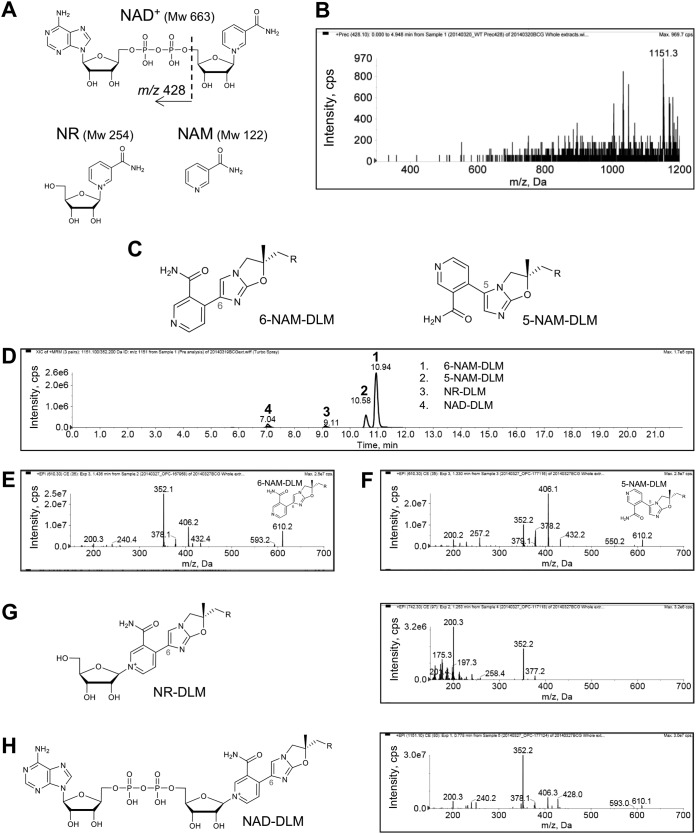
FIG 3.
Comparative analysis of predicted DLM-binding molecule candidates using chemically synthesized 5-NAM-DLM, 6-NAM-DLM, 6-NR-DLM, and 6-NAD-DLM. (A) Chemical structures of DLM-binding molecular candidates: NAD+ (MW, 663) and its component molecules, nicotinamide-riboside (NR; MW, 254) and nicotinamide (NAM; MW, 122) predicted with the Reaxys database and based on mass sizes of the peaks. The structure of ADP (m/z 428) is indicated. (B) Precursor ion scan for m/z 428 of DLM-treated WT BCG extract. The precursor ion of m/z 1,151, which corresponds to peak G, is indicated. (C) Chemical structures of 6-NAM-DLM (chemical formula C31H30F3N5O5; exact mass, 609.2199 Da) and 5-NAM-DLM (chemical formula C31H30F3N5O5; and exact mass, 609.2199 Da). (D) Ion chromatogram of synthesized 6-NAM-DLM (1), 5-NAM-DLM (2), 6-NR-DLM (3), and 6-NAD-DLM (4). (E and F) Product ion spectra of synthesized 6-NAM-DLM (E) and 5-NAM-DLM (F). (G) Chemical structure and product ion spectrum of 6-NR-DLM (chemical formula C36H39F3N5O9+; exact mass, 742.2700 Da). (H) Chemical structure and product ion spectrum of 6-NAD-DLM (chemical formula C46H52F3N10O18P2+; exact mass, 1,151.2888 Da). R = 4-(4-[4-trifluoromethoxyphenoxy]piperidin-1-yl)phenoxy group.