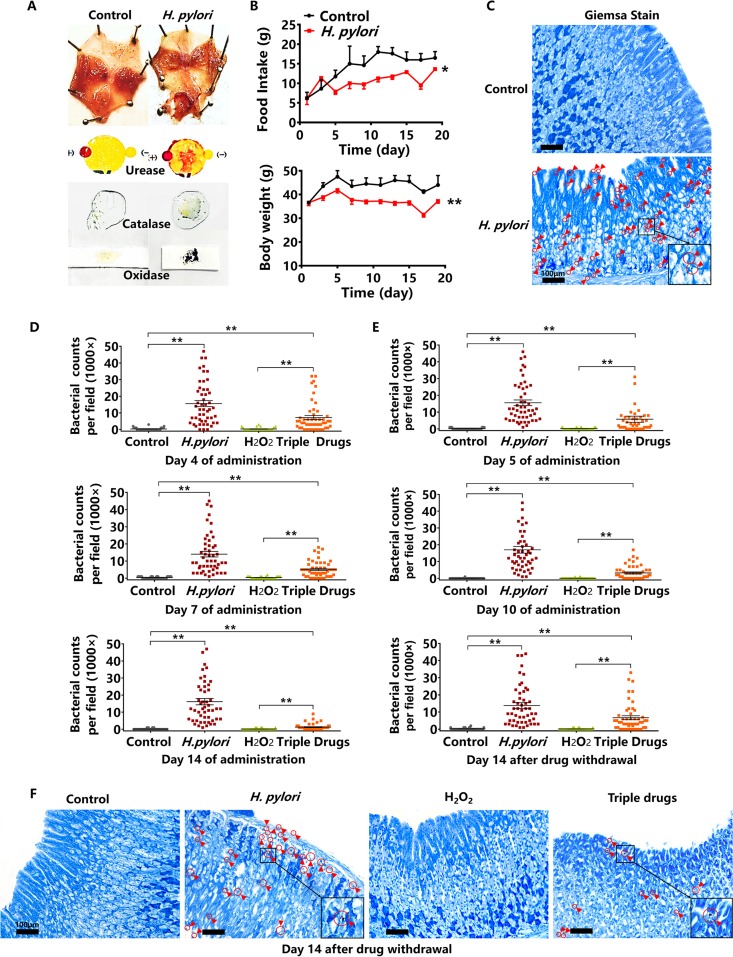
FIG 4.
The effect of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on H. pylori-infected Kunming mice. (A) The morphology of H. pylori-infected mucosa and assays for urease, catalase, and oxidase (H. pylori ATCC 43504). (B) The alterations of daily food intake and body weight of H. pylori-infected Kunming mice (H. pylori ATCC 43504). (C) Giemsa staining of H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Giemsa staining shows H. pylori as purple and gastric mucosa as blue. (D) The bacterial counts of H. pylori-infected mucosa on the 4th, 7th, and 14th days of oral administrations of hydrogen peroxide at 2 mg/ml. The triple-drug group was the positive control. (E) The bacterial counts of H. pylori-infected mucosa on the 5th and 10th days of oral administrations of hydrogen peroxide at 2 mg/ml, and on the 14th day after hydrogen peroxide withdrawal. (F) Giemsa staining of gastric mucosa on the 14th day after hydrogen peroxide withdrawal. Red circles and arrows indicate H. pylori ATCC 43504, as magnified within the black frame (n = 10 animals; 5 dots per animal; 50 dots per group). Values given are mean ± SE; *, P < 0.05; and **, P < 0.01 versus control, as determined by one-way ANOVA and Student’s t test.