FIG 1.
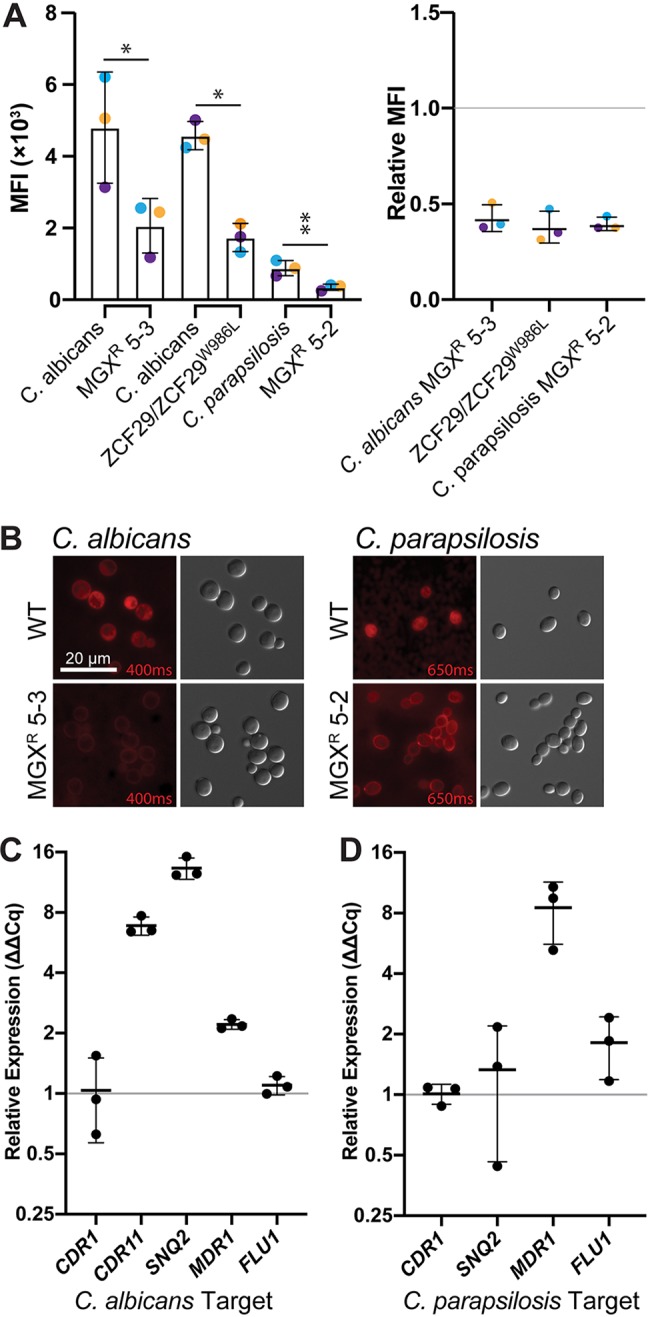
Drug efflux is activated in mutants of C. albicans and C. parapsilosis with reduced susceptibility to MGX. (A) C. albicans 5-3 and C. parapsilosis 5-2 mutants have reduced accumulation of the general efflux pump substrate Nile red. Nile red fluorescence was monitored by flow cytometry. (Left) Median fluorescence intensity (MFI; PE) ± standard deviation (SD) measured in 3 independent experiments (10,000 events/sample). (Right) Ratios of median fluorescence intensity for indicated mutant-wild type pair. Differences between groups were determined by ratio paired t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.005. Colored points indicate experimental replicates. (B) Representative micrographs of C. albicans and C. parapsilosis wild-type strains and mutants with decreased MGX susceptibility stained with Nile red, prepared the same as for those in panel A. Exposure times (milliseconds) are indicated in red. (C) Relative transcript levels of CDR11, SNQ2, and MDR1 but not CDR1 or FLU1 are upregulated in C. albicans MGXr 5-3. RT-qPCR data are mean fold changes ± SDs from 3 biological replicates assayed in technical triplicates, normalized to ACT1 and GPD1. (D) Transcript levels of MDR1 but not CDR1, SNQ2, or FLU1 are upregulated in C. parapsilosis MGXr 5-2. Experiments were performed the same as for those in panel C and normalized to ACT1.
