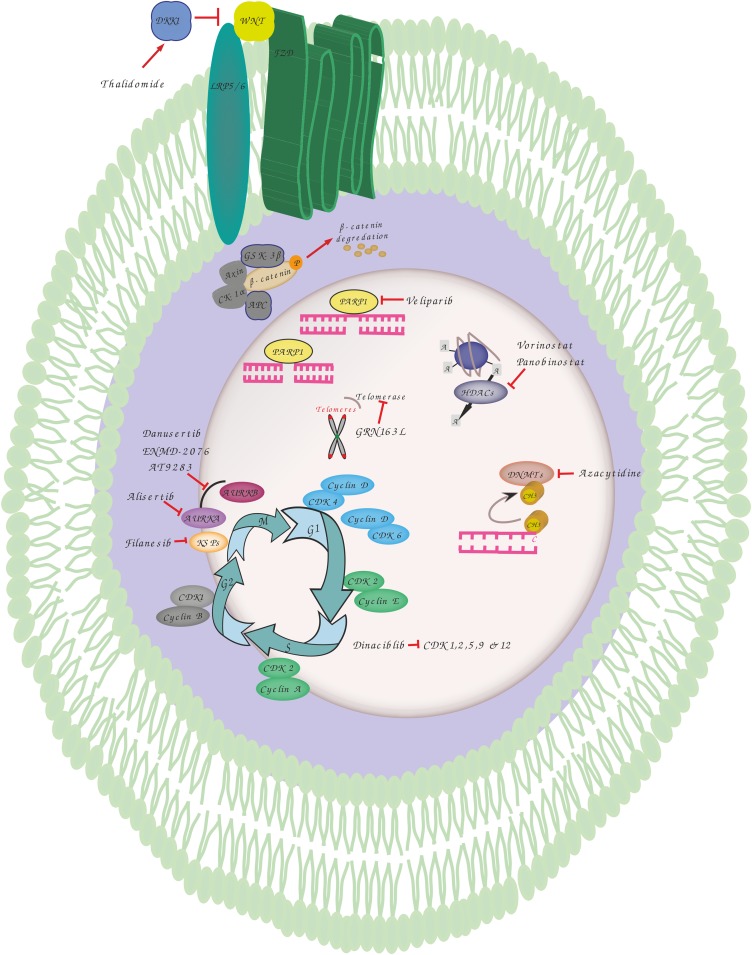
FIGURE 1.
Overview of genomic instability targets and relevant drugs. Thalidomide induces dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 1 (DKK1) that blocks the interaction between frizzled (FZD) receptors and lowdensity lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) resulting in phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of b-catenin by destruction complex including adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), Axin and casein kinase 1 alpha (CK1α). Veliparib inhibits poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) involved in various DNA repair pathways and in the maintenance of genomic stability. Vorinostat and Panobinostat are inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDACs) that catalyze the removal of the acetyl moiety from the lysine residues of histones and non-histone proteins. Azacytidine is used to inhibit the activity of DNA methyltransferases which catalyze DNA methylation of cytosine resulting in transcriptional inhibition and gene silencing. GRN163L is an inhibitor of telomerase which prevents the shortening of telomeres length. Dinaciblib inhibits the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 1, 2, 5, 9, and 12 that play essential roles in cell cycle regulation. Filanesib inhibits kinesin spindle protein (KSP) which is important for the proper separation of spindle poles during mitosis. Alisertib (MLN8237) is a selective aurora A kinase (AURKA) inhibitor, while Danusertib, ENMD-2076 and AT9283 act by inhibiting both AURKA and B that have essential roles in mitosis.