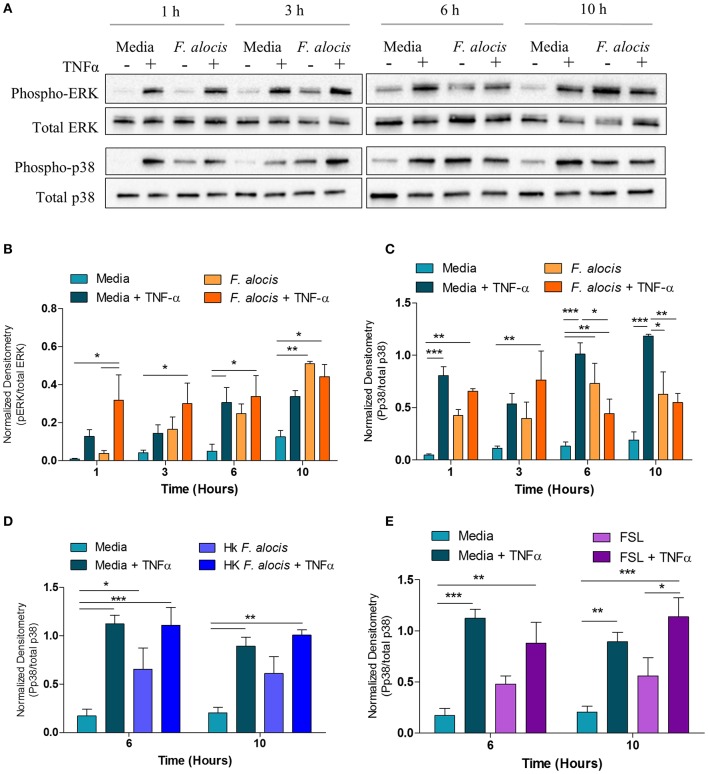
Figure 5.
F. alocis effect on TNFα-induced MAPK activation. Human neutrophils were cultured in media with or without F. alocis at an MOI of 10 for 1, 3, 6, or 10 h followed by stimulation with TNF-α for 15 min. Western blots with whole cell lysates were probed for phosphorylated and total p38 and ERK1/2 (A) and quantified by densitometry (B,C). To determine if the decreased p38 phosphorylation at 6 and 10 h was specific to the viable bacteria or a consequence of TLR 2/6 ligation, neutrophils were cultured in media alone, media with heat-killed F. alocis (D) or the TLR2/6 agonist FSL (E) for 6 or 10 h before TNF-α stimulation. Western blots of whole cell lysates were probed for phosphorylated and total p38. Densitometries are plotted as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical differences among experimental conditions and time points were analyzed by a repeating measures two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni post-tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.