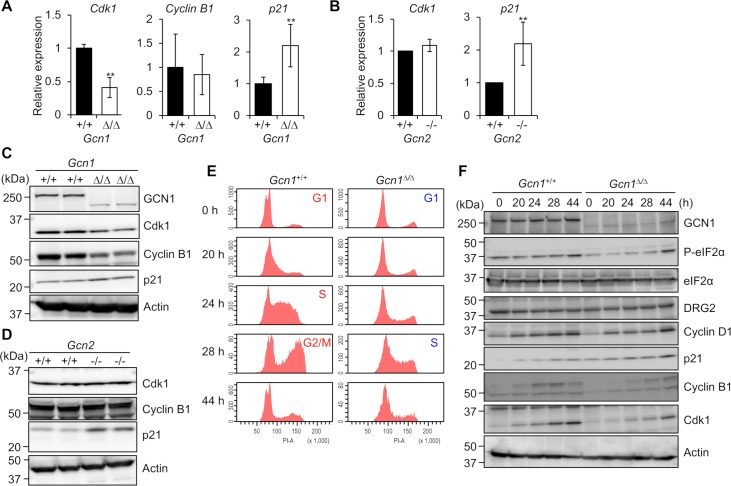
Fig 6. Expression of cell cycle regulation factors in Gcn1ΔRWDBD MEFs.
(A) (B) Gene expression levels related to cell cycle progression in the Gcn1ΔRWDBD MEFs (A) and Gcn2 KO (Gcn2-/-) MEFs (B) were quantified by RT-PCR. The value for wild-type cells was set to 1, and the results are shown as the relative folds±SD from multiple independent experiments ((A): N = 4, (B): N = 4). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 compared with the WT (two tailed Student’s t-test). (C) Whole cell proteins extracted from the WT (Gcn1+/+) and Gcn1ΔRWDBD MEFs were subjected to immunoblotting to detect GCN1, Cdk1, Cyclin B1, p21 and β-actin. (D) Whole cell proteins extracted from the WT (Gcn2+/+) and Gcn2 KO (Gcn2-/-) MEFs were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect Cdk1, Cyclin B1, p21 and β-actin. (E) Cell cycle analysis of the MEFs. WT (Gcn1+/+) and Gcn1ΔRWDBD MEFs were synchronized at G0-G1 by serum deprivation for 72 h. After serum stimulation at the indicated times, the cells were treated with PI, and the cell content was analyzed using flow cytometry. (F) Whole cell protein extracts from the WT (Gcn1+/+) and Gcn1ΔRWDBD MEFs obtained by the experiment in (E) were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect GCN1, phosphorylated eIF2α (P-eIF2α), eIF2α, DRG2, Cyclin D1, p21, Cyclin B1, Cdk1 and β-actin.