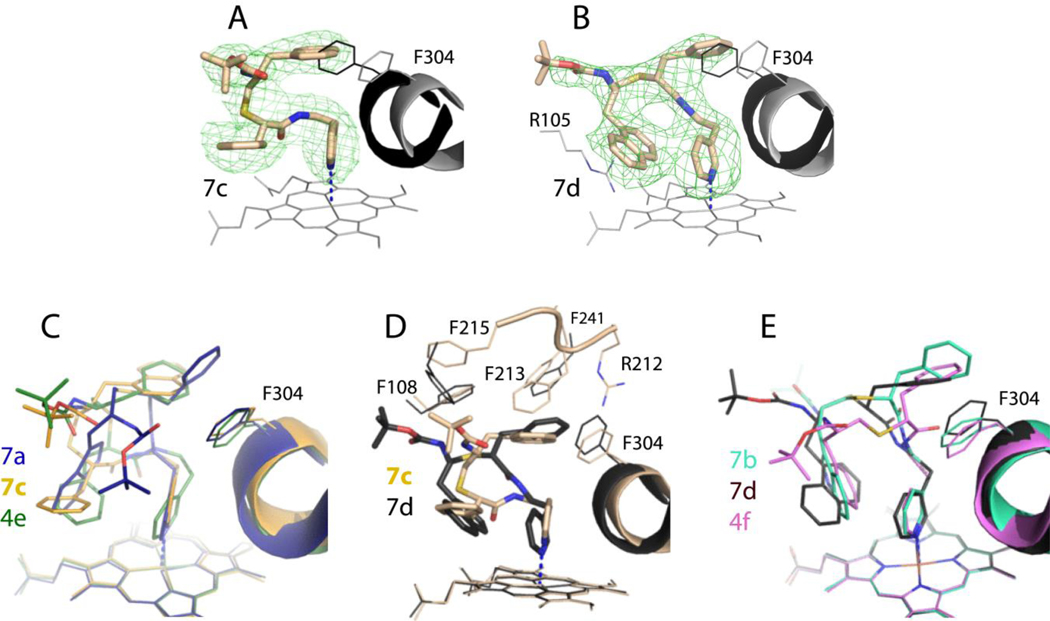
Figure 6.
A and B, The binding mode of 7c and 7d, respectively. The adjacent I-helix and F304 in the inhibitory complexes and water-bound CYP3A4 (4I3Q structure) are shown in black and gray, respectively. Polder omit maps contoured at 3σ level are shown as green mesh. The CYP3A4-7c complex crystallizes in a distinct space group (Table S2) with two molecules per asymmetric unit; the better-defined molecule A was used for structural comparison.
C, Superposition of the 7a-, 7c- and 4e-bound structures of CYP3A4 (6UNH, 6UNJ and 6DAB, respectively). 4e is a series III inhibitor with a similar backbone and R1/R2-phenyls in S/R configuration.
D, Superposition of the 7c/d-bound CYP3A4.
E, Superposition of the 7b-, 7d- and 4f-bound structures of CYP3A4 (6UNI, 6UNK and 6DAC, respectively). 4f is a series III inhibitor with a similar backbone and R1/R2-phenyls in R/S configuration.