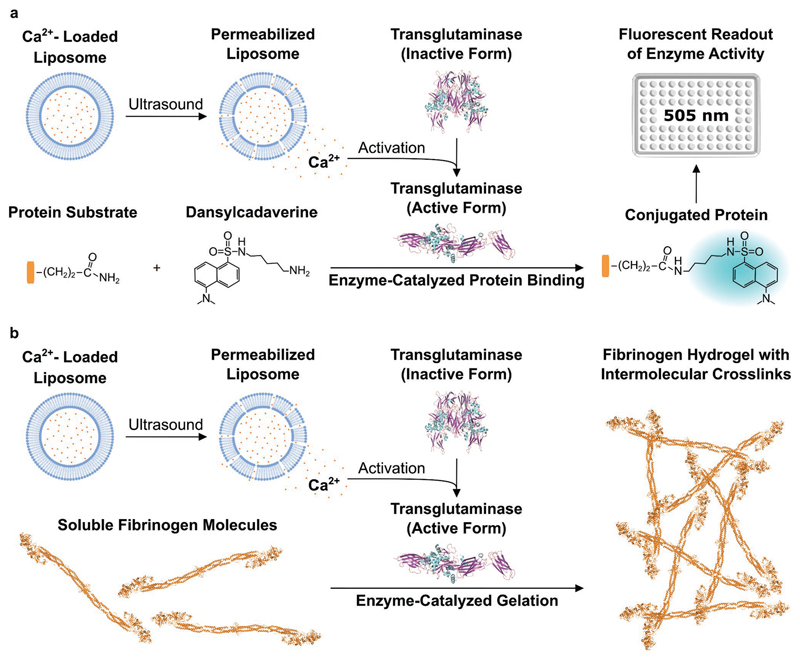
Figure 1. Schematic of ultrasound-triggered enzyme catalysis and hydrogelation.
a) Ultrasound is applied to calcium-loaded liposomes in order to liberate calcium ions and activate transglutaminase. The active transglutaminase then catalyzes isopeptide bond formation between a protein substrate and dansylcadaverine. This conjugation produces a shift in the maximum fluorescence emission wavelength of dansylcadaverine and an increase in fluorescence intensity at 505 nm. b) A similar ultrasound-triggered process is used to catalyze the crosslinking of soluble fibrinogen molecules. In this scenario, intermolecular crosslinking is used to generate fibrinogen hydrogels. The graphics for the structures of inactive and active transglutaminase and of fibrinogen were adapted from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and processed with Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) software. Inactive transglutaminase PDB ID: 1kv3; active transglutaminase PDB ID: 2q3z; fibrinogen PDB ID: 3ghg.[30] The graphics for the 96-well plate were adapted from the Servier Medical Art website.