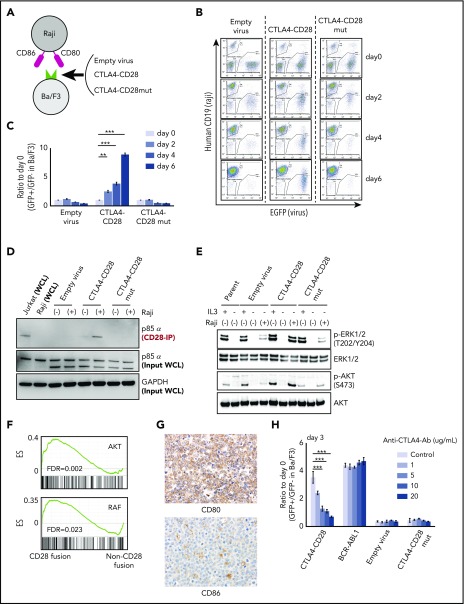
Figure 2.
Functional analysis of CTLA4-CD28 fusion. (A) Cartoon depicting an assay in which Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty virus, virus expressing CTLA4-CD28, or virus expressing CTLA4-CD28 with a loss of function (CTLA4-CD28mut) were cocultured with irradiated Raji cells that express CD80 and CD86. (B) Representative results of Ba/F3-Raji assay without mouse IL-3. x-axis indicates enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) as a marker of transduced Ba/F3 cells; y-axis indicates human CD19 expression marking Raji cells. Note that Ba/F3 cells expressing CTLA4-CD28 (GFP+hCD19−) but not Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty virus or CTLA4-CD28mut are present at days 4 and 6. (C) Normalized ratios of EGFP+ fractions in Ba/F3 to those on day 0. The differences were evaluated by 1-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. Data are presented as means plus or minus standard deviation (SD) from 4 independent experiments, with each performed in triplicate. (D) Western blotting of anti-CD28–immunoprecipitated (IP) samples and whole-cell lysate (WCL) from indicated cell lines. (E) Western blotting of Ba/F3 cells expressing CTLA4-CD28, CTLA4-CD28mut, or empty virus with or without IL3 and Raji cells. (F) GSEA plots of indicated gene sets in the analyzed ATLL cases with or without CD28 fusions. (G) Immunohistochemical features of case 10658 stained for CD80 and CD86. Upper panel shows the image of CD80 stain and lower panel represents that of CD86 stain; original magnification, ×400 for both panels. (H) Normalized ratios of green fluorescent protein–positive (GFP+) Ba/F3 fractions compared with day 0 in the presence of Raji cells and increasing doses of anti-CTLA4 antibody. Data are presented as means plus or minus SD from 4 independent experiments, with each performed in triplicate. The differences were evaluated by 1-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction. ***P < .001. Ab, antibody; ES, enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; p-AKT, phosphorylated AKT; p-ERK, phosphorylated ERK.