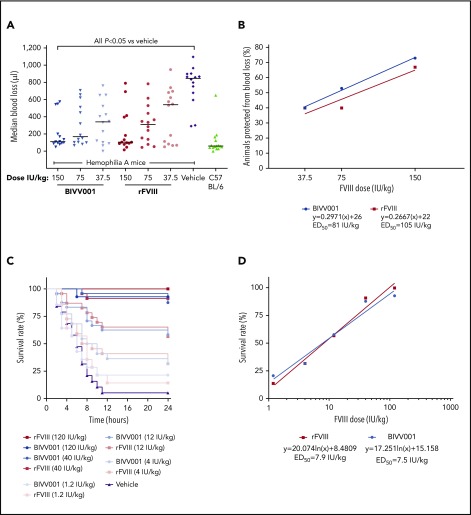
Figure 6.
Efficacy of BIVV001 in HemA mice. (A,B) Acute hemostatic efficacies of BIVV001 (37.5, 75, and 150 IU/kg; all IV and n = 14 for each dose), equivalent doses of rFVIII (n = 14 for each dose), and vehicle (n = 14) were evaluated in HemA mice in an acute-blood-loss, tail-clip model. C57BL/6 mice (n = 15) served as the positive control. (A) Individual median blood loss over 30 minutes was quantified gravimetrically and compared between groups with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov t test. Horizontal bars are medians. (B) The state of being “protected” was granted if blood loss was less than or equal to the mean volume of blood lost by C57BL/6 mice in the tail-clip model. The ED50 was the dose of each treatment that achieved protection from acute bleeding in 50% of treated animals. ED50 values were 81 IU/kg for BIVV001 and 105 IU/kg for rFVIII. (C) The effect of prophylactic single-dose BIVV001 (1.2-120 IU/kg; IV), equivalent doses of rFVIII, and vehicle on 24-hour survival rates of HemA mice (n = 15-20 per dose group) after tail vein transection were assessed. BIVV001 and rFVIII were administered at 96 and 24 hours, respectively, before tail vein transection. (D) Twenty-four-hour survival rates after BIVV001 and rFVIII administration were compared with those obtained with vehicle (log-rank Mantel-Cox test). FVIII led to significantly higher survival rates at 24 hours after TVT (P < .05) compared with vehicle. Direct survival comparison showed no significant difference between BIVV001 and rFVIII, indicating that BIVV001 is comparable to rFVIII; n = 15 to 20 mice per group. Similar survival protection ED50 values for BIVV001 and rFVIII were calculated by the nonlinear fit equation.