FIGURE 7.
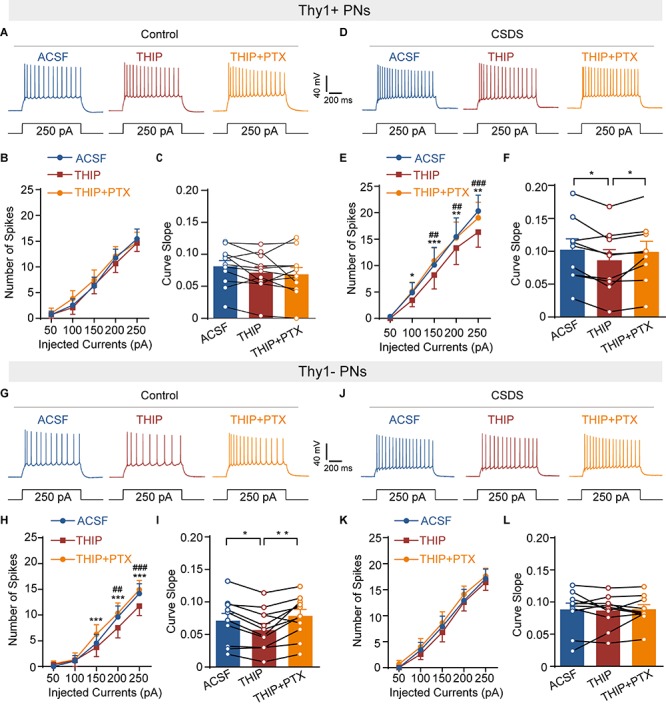
Chronic social defeat stress increases GABAergic modulation of neuronal excitability of Thy1+ neurons but decreases those of Thy1- neurons in amygdala. (A) Representative traces of the firing pattern of a Thy1+ neuron in control mice in response to current injections (250 pA, 1 s) when the slice was perfused with ACSF, THIP, and THIP+ PTX successively. (B) Summary plots of the spikes number as a function of current strength, as in (A). (C) Comparisons of the curve slope in (B). (D) Same illustrations as in (A) except the data were obtained from CSDS mice. (E) Summary plots of the spikes number as a function of current strength, as in (D). (F) Comparisons of the curve slope in (E). (G) Same as in (A) except that the data were collected from Thy1- neurons. (H) Summary plots of the spikes number as a function of current strength, as in (G). (I) Comparisons of the curve slope in (H). (J) Same plotting of neuronal firing as in (D) except the data were obtained from Thy1- neuron. (K) Summary plots of the spikes number as a function of current strength, as in (J). (L) Comparisons of the curve slope in (K). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. THIP + PTX group/THIP group, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. ACSF group by THIP group. Pooled data are presented as mean ± SEM.
