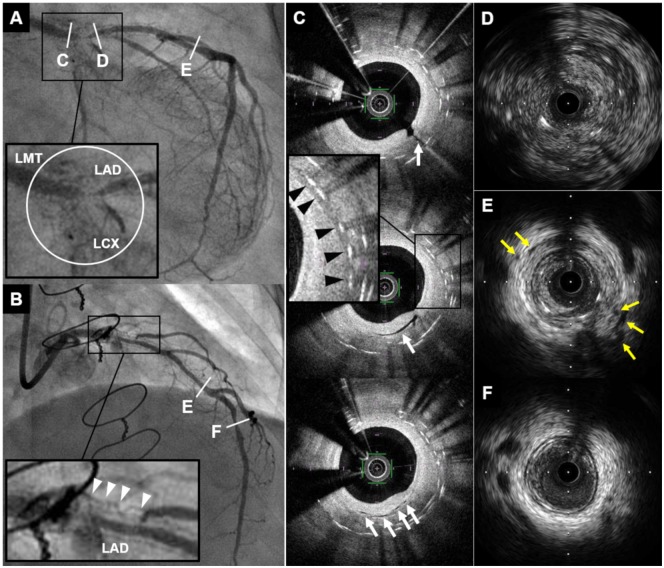
Figure 1.
Coronary angiogram and intracoronary imaging findings of Case 1. (A and B) Coronary angiogram demonstrated severe in-stent restenosis with remarkable proliferated neovascularization around the stented segment (white circle and white arrowheads) in distal left main trunk to ostium of left anterior descending artery and left circumflex coronary artery. (C) Optical coherence tomography revealed multiple microvessels communicating with lumen (white arrows) and peri-strut low intensity area (black arrowheads) within neointima. (D–F) Intravascular ultrasound showed ambiguous three-layered structure within the stented and non-stented segments (D), and various degrees of peri-arterial low-echoic area and peri-arterial small vessels (yellow arrows) within stents and near distal stent edge (E). In contrast, these findings were not apparent in distal left anterior descending artery (F). CAG, coronary angiography; IVUS, intravascular ultrasound; LAD, left anterior descending artery; LCX, left circumflex coronary artery; LMT, left main trunk; OCT, optical coherence tomography; PLEA, peri-arterial low-echoic area.