Figure 5.
Interactions between RG-Rich and Autoinhibitory Acidic IDRs Regulate G3BP1 Phase Separation
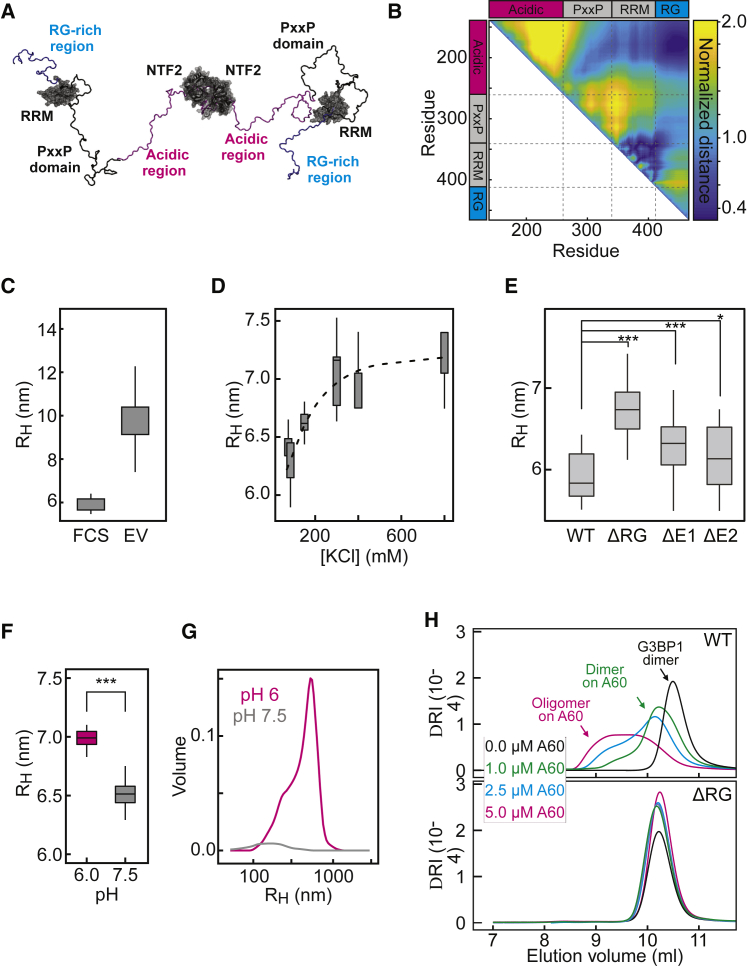
(A) Conformational snapshot of G3BP1 from an excluded volume (EV) simulation (instantaneous RH, ∼11 nm).
(B) Normalized distance between any pair of residues in G3BP1(ΔNTF2) simulations. Cooler colors are closer together, and warmer colors are farther apart. Dashed lines delineate domains.
(C) RH for G3BP1 dimers, inferred from FCS measurements and EV simulations of full-length dimeric G3BP1 with generic, self-avoiding descriptions for the IDRs.
(D) RH of G3BP1(WT) as a function of KCl concentration, determined by DLS. Fit shown with a dashed line.
(E) RH of G3BP1 variants, determined by FCS.
(F) RH of G3BP1(WT) at pH 6 and pH 7.5, determined by DLS.
(G) Oligomeric species of G3BP1(WT) at pH 6 or pH 7.5, detected by DLS. Shown is the mean average (n = 30).
(H) Analytical gel filtration of G3BP1(WT) and G3BP1(ΔRG) on A(60) RNA as a function of RNA concentration.
Significance levels: ∗ < 0.05, ∗∗ < 0.01, ∗∗∗ < 0.001. See also Figure S5.