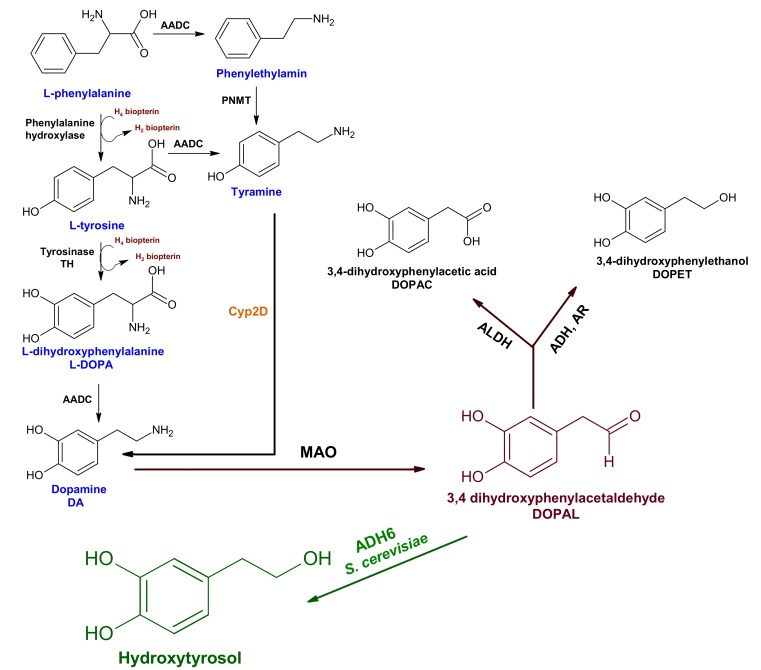
Figure 7.
Proposed pathway for the endogenous production of hydroxytyrosol from DOPAL in PC12 cells. In eukaryotes, DA is synthesized via the classical and nonclassical pathways. In the classical pathway, phenylalanine is hydroxylated into tyrosine by phenylalanine hydroxylase and converted into L-DOPA by the action of tyrosinase. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-DOPA into DA. The nonclassical pathway of DA biosynthesis starts with L-phenylalanine decarboxylation into tyramine by AADC, and CYP2D catalyzes the oxidation of tyramine into DA. MAO catalyzes the degradation of DA into DOPAL (an endogenous neurotoxin), which is further degraded into DOPAC (major product) and DOPET (minor product) (written in black). ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase), AR (aldehyde reductase), and ALDH (aldehyde dehydrogenase). In this study, we introduced ADH6 (S. cerevisiae) for the efficient conversion of DOPAL into the hydroxytyrosol and relief of OS (written in green).