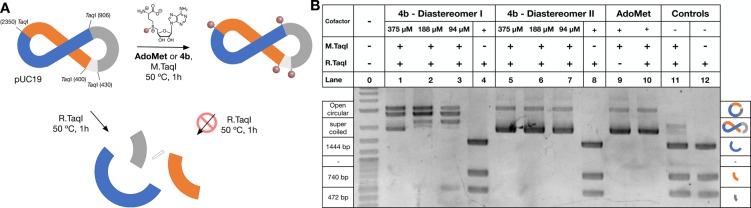
Figure 2.
MTase-directed labeling of plasmid DNA. (A) Schematic representation of restriction assay and (B) gel electrophoresis of pUC19 following enzymatic treatment with M.TaqI and/or R.TaqI in the presence and absence of AdoMet (375 μM) or AdoMet derivative 4b. In the absence of M.TaqI-mediated alkylation (lanes 4, 8, and 12), pUC19 is cut into fragments, of which the largest three can be identified by gel electrophoresis. M.TaqI-mediated alkylation with AdoMet (line 10) or derivative 4b (lanes 1–3 and 5–6) results in partial to full protection from restriction by R.TaqI, with mainly open circular and supercoiled plasmid DNA being observed by gel electrophoresis. Controls in the absence of AdoMet derivatives (lanes 11 and 12), in the absence of M.TaqI (lanes 4, 8, and 12) and in the absence of R.TaqI (lane 9) are included.