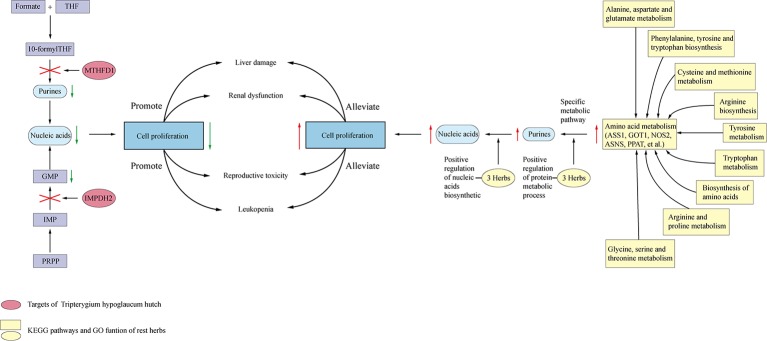
Figure 6.
The mechanism of side effect caused by Tripterygium hypoglaucum hutch and the mechanism of alleviation compensated by the rest of herbs. Tripterygium hypoglaucum hutch may inhibit the activity of IMPDH2 which encodes the rate-limiting enzyme (inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase) in the de novo guanine nucleotide biosynthesis. As a result, the metabolism of nucleic acid was inhibited because of the downregulation of guanine. Besides, Tripterygium hypoglaucum hutch may inhibit the activity of MTHFD1 which encodes a protein that possesses the folic acid metabolism related enzymes activities, disrupting the purines converted to nucleic acid. The rest herbs could act on ASS1, GOT1, NOS2 et al. in the amino acid metabolism pathways, including glycine, serine, and threonine and form a positive regulation of amino acid. After that amino acid could be changed to purines via specific metabolic pathway, which compensating purines metabolic disrupted by Tripterygium hypoglaucum hutch. Besides, the rest herbs could play roles in positive regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated, positive regulation of RNA biosynthetic process, helping in the transition of purines to nucleic acid.