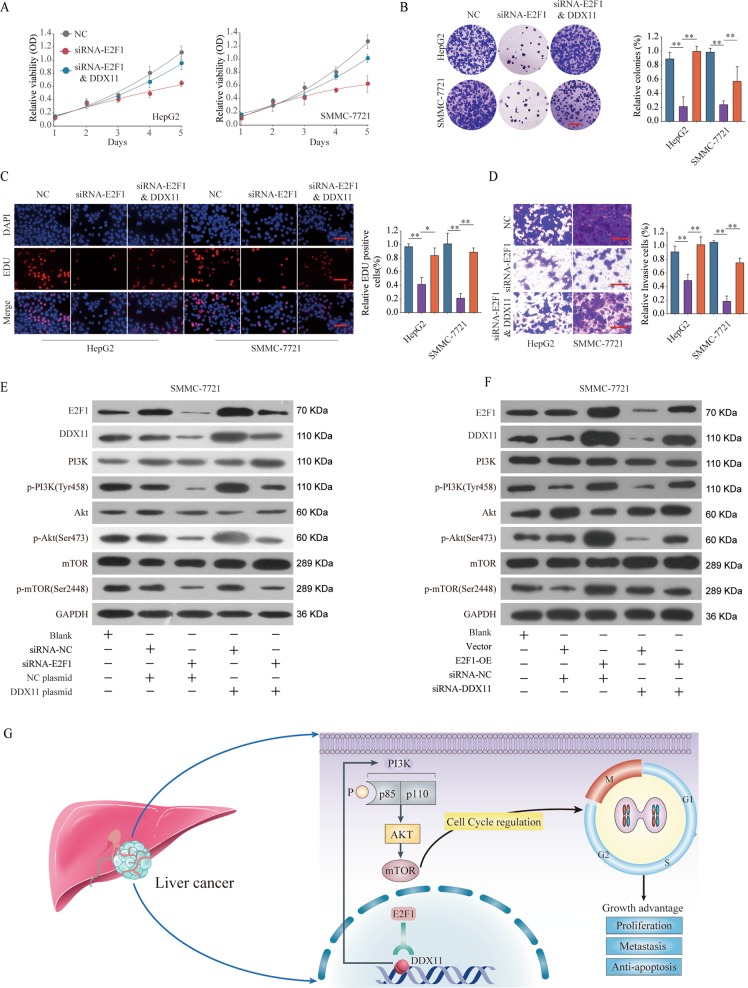
Fig. 8. E2F1/DDX11 axis contributes to HCC cell proliferation and invasion through activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
HepG2 or SMMC7721 cells were transfected with negative control (NC), siRNA targeting E2F1 (siRNA-E2F1), or siRNA-E2F1 & DDX11 overexpression plasmid (DDX11). a–c Cell proliferation of HepG2 or HuH-6 cells was assessed by CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay or EDU staining assay. Scale bars, 50 μm. d Cell invasion ability of HepG2 or SMMC7721 cells in different groups was analyzed by transwell assay. Scale bars, 50 μm. e Expression levels of PI3K/p-PI3K(Tyr458), Akt/p-Akt (Ser473), and mTOR/p-mTOR (Ser2448) in SMMC7721 transfected with negative control, siRNA-E2F1, negative control plasmid, or DDX11 plasmid were analyzed by western blot. f Expression levels of PI3K/p-PI3K(Tyr458), Akt/p-Akt (Ser473), and mTOR/p-mTOR (Ser2448) in SMMC7721 transfected with negative control, E2F1 plasmid, negative control siRNA, or DDX11 siRNA were analyzed by western blot. The representative result of at least three independent experiments was shown. g Schematic representation showing E2F1/DDX11 axis mediated aggressive behaviors in HCC through activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.