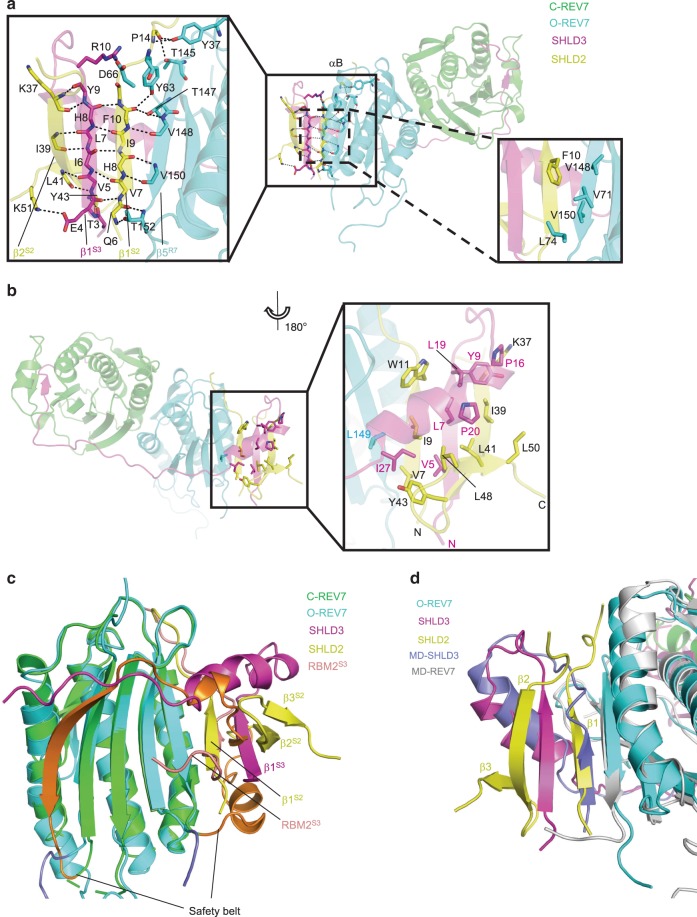
Fig. 6. Structural mechanism of SHLD2 recognition by O-REV7-SHLD3.
a Details of the hydrogen bond network (the left panel) and hydrophobic network (the right panel). In the detailed view, αB of O-REV7 and side chains that do not contribute to polar contacts are omitted for convenience to read. b Hydrophobic network in the reverse side rotated along y-axis compared with Fig. 6a. c Structural alignment of C-REV7-RBM2S3 and O-REV7-SHLD2-SHLD3. The regions between two lines represent safety belt and are colored in orange (C-REV7) and slate (O-REV7). RBM2S3 represents RBM2 of SHLD3 and is colored in salmon. The superscript S2 and S3 represents SHLD2 and SHLD3, respectively. d Molecular dynamics simulation results of the SHLD3-C-REV7-O-REV7 complex and structural alignment of SHLD3-REV7-SHLD2 complex and SHLD3-C-REV7-O-REV7 complex shows the interaction model of SHLD3 β1 and O-REV7. MD-SHLD3 and MD-REV7 shows structures of SHLD3 and O-REV7 after molecular dynamics simulation. The secondary structures of SHLD2 are labeled in detail.