Fig. 7. A proposed model for PpMACRO2 in chromatin modification and development of P. patens.
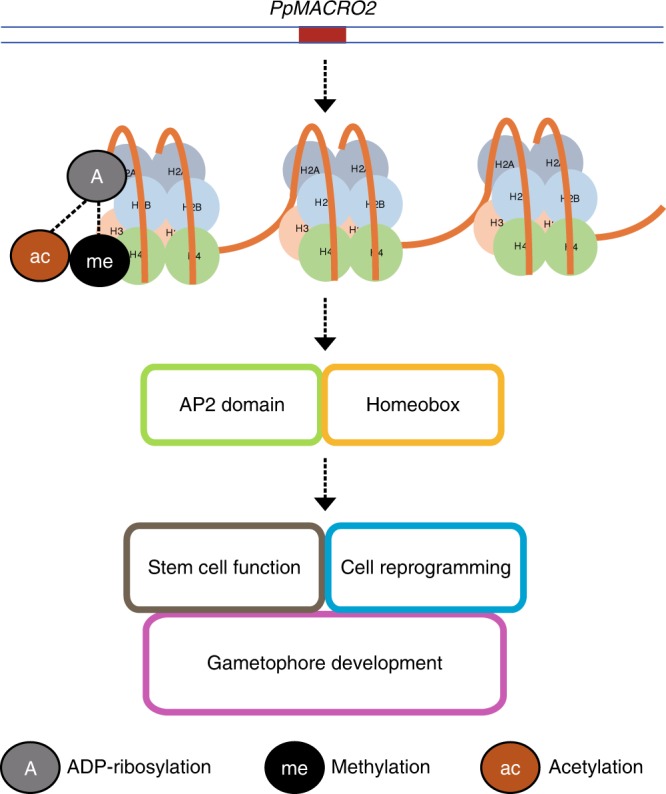
PpMACRO2 is likely involved in chromatin modification through ADP-ribosylation, which in turn triggers a cascade of additional chromatin changes via other epigenetic mechanisms, including histone methylation and acetylation. These epigenetic modification mechanisms may fine-tune chromatin conformation, which consequently activates/represses downstream developmental transcription factors (e.g., AP2 and homeobox) and affects stem cell function, cell reprogramming, gametophore development, and other biological processes. Dashed lines indicate that the relationship is less certain.
