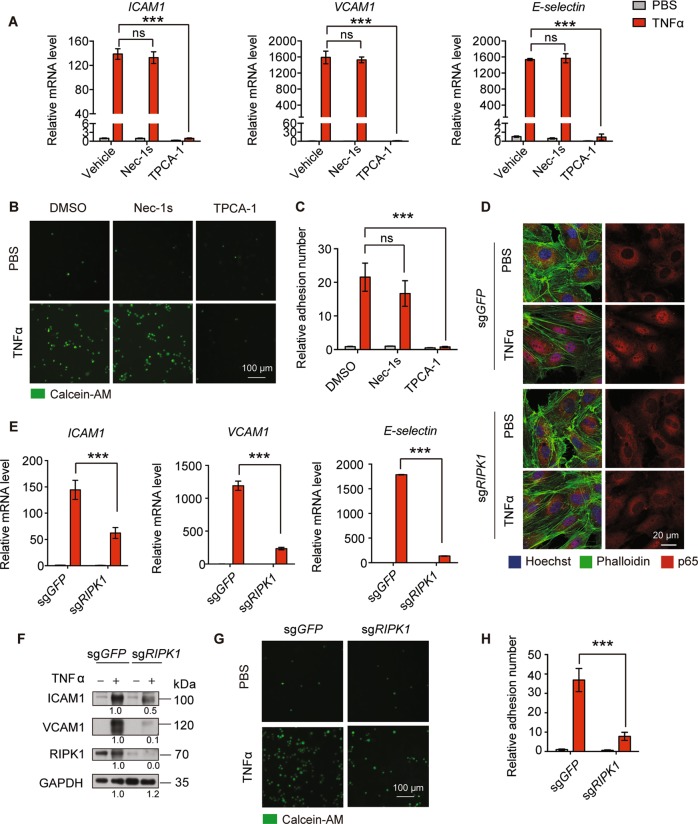
Fig. 3. MLKL regulates adhesion molecules expression is independent of RIPK1 kinase activity and RIPK1 mediated NF-κB activation.
a HUVEC were pretreated with Nec-1s (10 μM) or TPCA-1 (5 μM) for 1 h then were stimulated with TNFα (100 ng/ml) for 6 h. The expression levels of ICAM1, VCAM1, and E-selectin were determined by real-time PCR. b, c HUVEC were treated with Nec-1s (10 μM) or TPCA-1 (5 μM) for 1 h followed by TNFα (100 ng/ml) stimulation for 12 h and incubated with calcein-AM-labeled iBMDM for 30 min, then adherent iBMDM were imaged (b) and quantitated (c). Scale bar, 100 μm. d Control or RIPK1 knockout HUVEC were stimulated with TNFα (50 ng/ml) for 15 min and nuclear translocation of p65 was determined by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar, 20 μm. e, f Control or RIPK1 knockout HUVEC were stimulated with TNFα (50 ng/ml) for 6 h and then expression levels of adhesion molecules was determined by real-time PCR (e) and immunoblot (f). g, h Control or RIPK1 knockout HUVEC monolayers were first stimulated with TNFα (100 ng/ml) for 12 h, then incubated with calcein-AM-labeled iBMDM for 30 min and adherent iBMDM were imaged (g) and quantitated (h). Data are representative of three independent experiments, with each experiment containing biological triplicates. Mean ± SD; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant; Student’s t test. Scale bar, 100 μm.