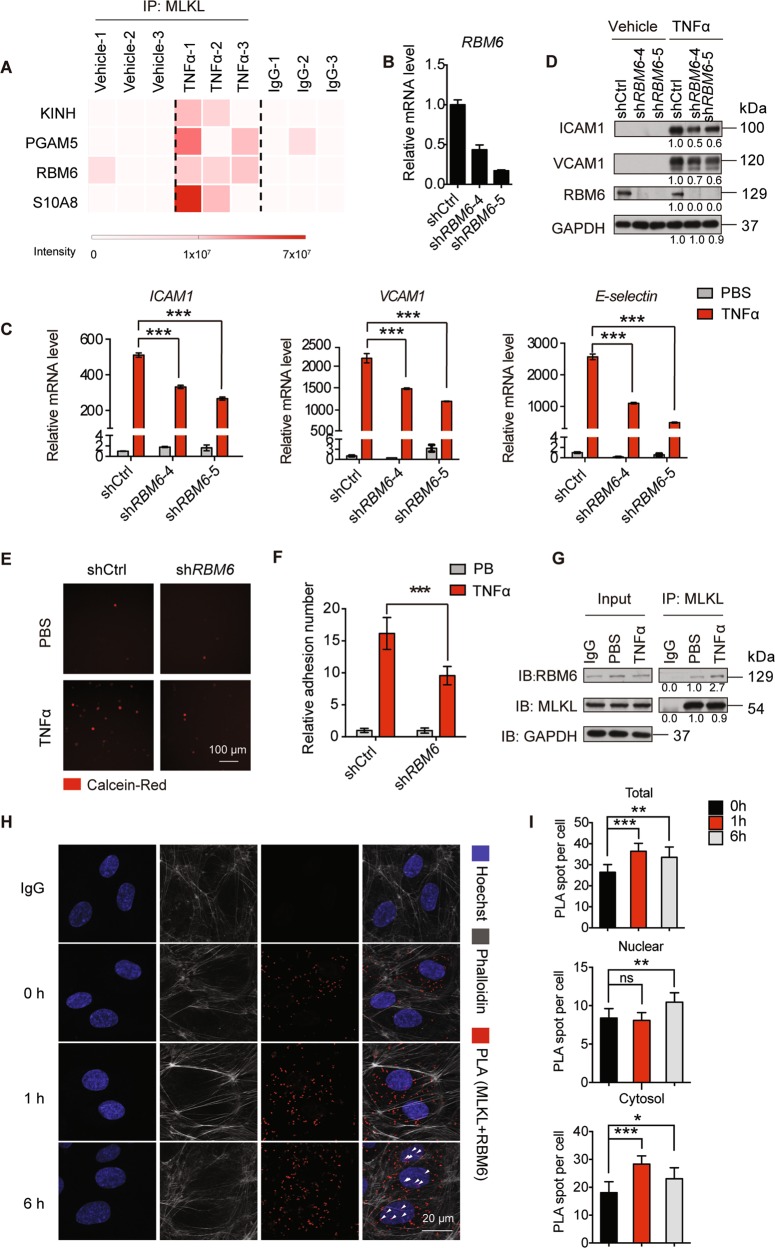
Fig. 5. MLKL interacts with RBM6.
a Heatmap showing the intensity of potential MLKL-interacting proteins identified by mass spectrometry (n = 3 biological replicates). b HUVEC were transduced with shCtrl or shRBM6 and the knockdown efficiency was validated by real-time PCR. c, d The expression of adhesion molecules in shCtrl or shRBM6 transduced HUVEC post TNFα (50 ng/ml) stimulation was determined by real-time PCR (c) and immunoblot (d). e, f Control or RBM6 shRNA transduced HUVEC monolayers were first stimulated with TNFα (100 ng/ml) for 12 h, then incubated with calcein-Red-labeled iBMDM for 30 min and adherent iBMDM were imaged (e) and quantitated (f). Scale bar, 100 μm. g–i The interaction of MLKL and RBM6 was confirmed by immunoprecipitation (g), and PLA (h). PLA spots were quantitated in (i). Arrowheads indicated the nuclear PLA signal. Hoechst, blue; Phalloidin, gray; PLA (MLKL and RBM6), red. Data are representative of three independent experiments, with each experiment containing biological triplicates. Mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant; Student’s t test. Scale bar, 20 μm.