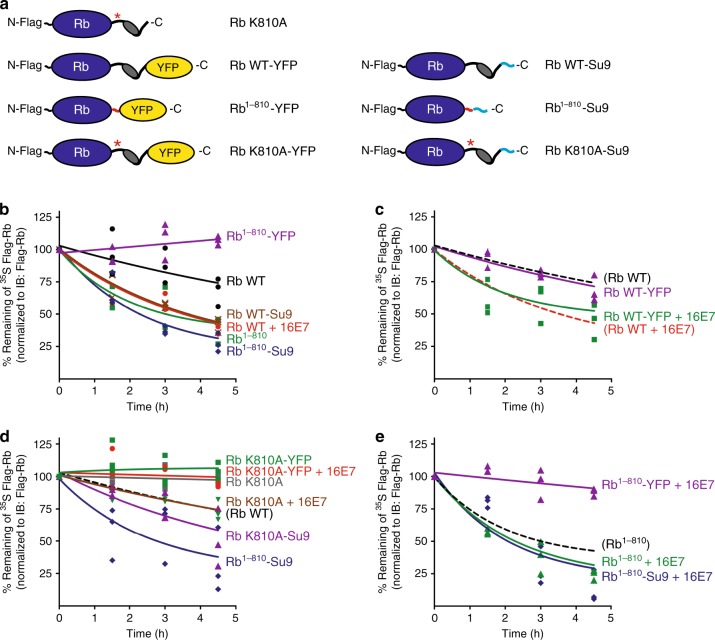
Fig. 2. The degradation of Rb is regulated by its C-terminus.
a Schematic view of Rb WT, Rb1–810, and the cleavage-resistant mutant of Rb in which Lys 810 was replaced with Ala (Rb K810A), with either YFP or an Su9 tail attached at their C-termini. The K810A mutation site, YFP, and Su9 tail are highlighted in red with an asterisk, in yellow, and in light blue, respectively. b–e Metabolic pulse chase of Rb in cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with Rb mutants (see Fig. 1b and a of the figure) and empty vector or 16E7 for 42 h. The cells were metabolically labeled with [35S] methionine/cysteine for the last 20 h, washed twice with PBS, and chased in label-free medium for the indicated times. Rb mutants were immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates and subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with Flag antibody and electronic autoradiography. The effects of modifications at the Rb C-terminus (b), of 16E7 expression (c, e), and of the K810A mutation (d) on the degradation rates of Rb were evaluated. Degradation of Rb WT, Rb WT + 16E7, and Rb1–810 were replotted in some panels with broken lines to help with comparisons. The graphs plot the relative band intensities over time as a percentage of the initial protein amount from three repeat experiments. Representative gel images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1a. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.