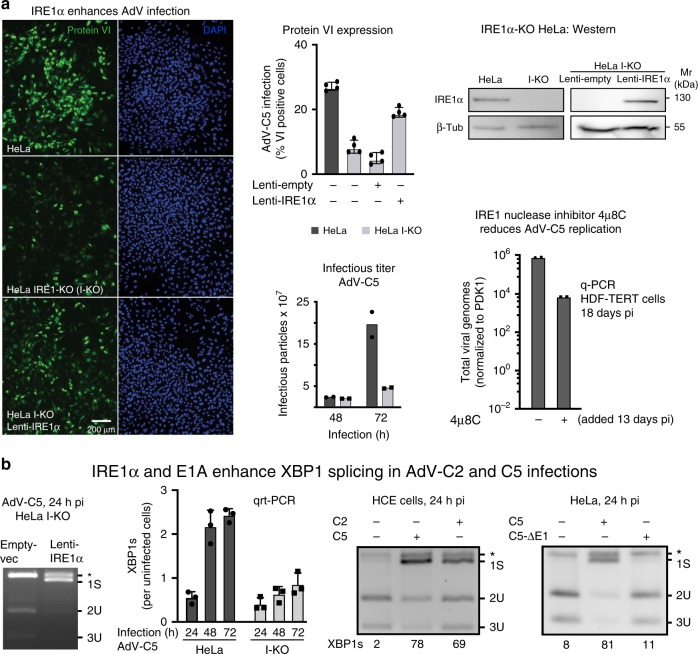
Fig. 1. IRE1α activation enhances AdV infection of HeLa cells.
a IRE1α-knockout (I-KO) HeLa cells are less susceptible to infection by AdV-C5 (MOI 75, 75 vp/cell) compared with normal HeLa, as indicated by late viral protein VI expression, whereas the ectopic lentivirus-mediated expression of IRE1α in HeLa I-KO cells restores infection (left panel, upper row middle and right panels showing representative images and quantifications, respectively. Scale bar, 200 µm). Data show the means ± SD from four independent experiments. Reduced virus growth in HeLa I-KO cells compared with wild-type cells. Cells were infected with AdV-C5 (MOI 500) for 1 h at 37 °C (equivalent to MOI 50 in continuous infection), unbound virus washed off, and virus titers from cells and supernatant measured at 48 and 72 hpi (lower row middle panel). Data show the means from two independent experiments. The IRE1α endonuclease inhibitor 4µ8C reduces AdV-C5 titers in long-term infections of HDF-TERT cells (lower row, right panel). HDF-TERT cells were infected with AdV-C5 (MOI 200, 37 °C, 1 h), followed by addition of 4µ8C (100 µM) 13 days pi. Data show the means from two independent experiments. b. IRE1α and the expression of the viral E1A protein are required to enhance XBP1 splicing in AdV-C2 and C5 infections. Rescue of XBP1 splicing in AdV-infected I-KO cells by IRE1α overexpression (first panel). Cells were transduced and infected as in a; cell lysates were subjected to XBP1 splicing assays at 24 hpi. Reduced XBP1s transcripts in HeLa I-KO compared with normal HeLa cells upon AdV-C5 infection (MOI 5, second panel). Data show the means ± SD from three independent experiments. XBP1 splicing in human conjunctival epithelial cells infected with AdV-C2 or C5 (MOI 75, third panel). E1A-deleted AdV-C5 mutant does not activate XBP1 splicing in HeLa cells 24 hpi (MOI 200 each, fourth panel). The asterisk denotes a background product. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.