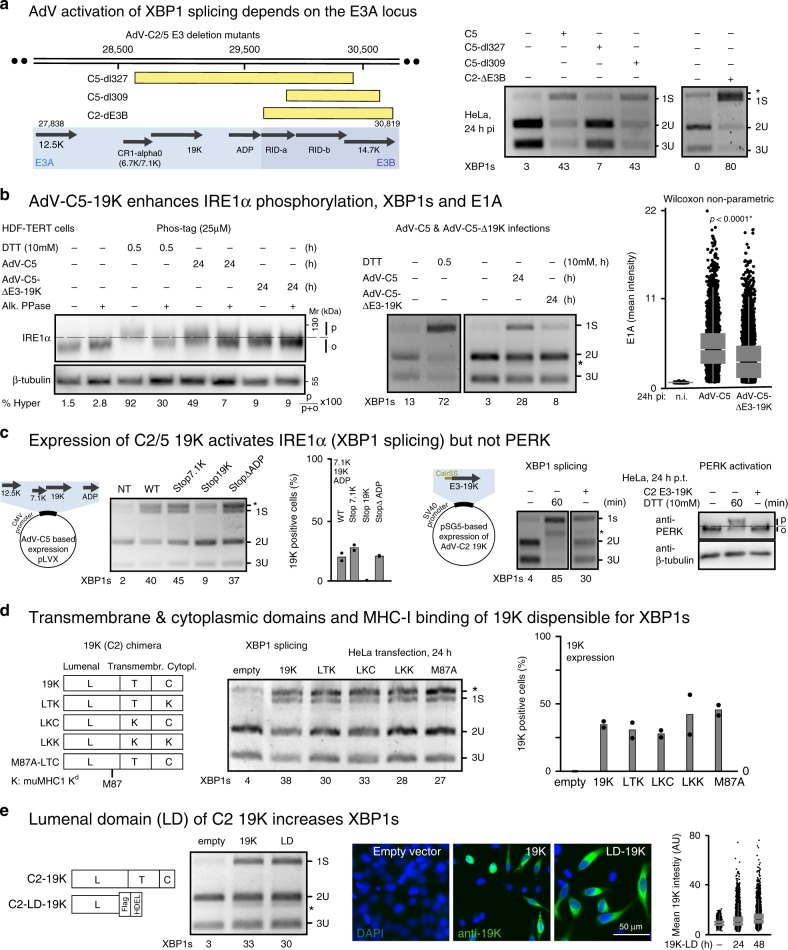
Fig. 3. The lumenal domain of the 19K glycoprotein activates IRE1α.
a Schematic drawing showing the deletions in the E3 region of AdV mutants with yellow boxes indicating the deletions (left panel). Infection was carried out with a median of 150 particles bound per cell. Asterisk denotes a background product. At least three independent experiments gave similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b AdV-C5 19K enhances IRE1α phosphorylation, XBP1s splicing, and E1A levels. Phosphorylation of IRE1α in AdV-C5- and AdV-C5-d19K-infected HDF-TERT cells (MOI 75000, 24 hpi) was analyzed in lysates treated with or without alkaline phosphatase, and fractionated by SDS-PAGE (6%, containing 25 µM Phos-tag, first panel). XBP1 splicing in AdV-C5- and AdV-C5-d19K-infected HDF-TERT cells 24 hpi (MOI 75,000, second panel). Immunofluorescence data of E1A are shown as a scatterplot using n = 14,000 cells randomly chosen per condition, 24 hpi (MOI 75000). Central line of the box plot indicates median with first and third quartiles, and whiskers are shown as boxes and lines, respectively. Statistics were performed using the Wilcoxon two-sided nonparametric test with *p < 0.0001 (third panel). Three independent experiments gave similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c Schematic depiction of lentiviral vectors expressing the AdV-C2 E3A locus open-reading frames (left panel). Premature termination of C2 E3A genes encoding the membrane proteins 7.1K, and ADP maintains XBP1s induction, whereas premature termination of 19K abolishes it (second panel). Data show the means from two technical replicates. Two independent experiments gave similar results. The western blot in the last panel displays activated phosphorylated (p) and unphosphorylated PERK (o). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d Chimeric and mutant 19K constructs lacking transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains or the MHC-I binding site (M87A mutant) can induce XBP1s (left and middle panels). The wild-type lumenal, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains are labeled as L, T, and C, respectively, whereas mutant murine MHC-I domain replacing them is labeled as K56. The relative 19K expression levels in HeLa cells are shown in the right panel after Tw1.3 staining. Data are presented as mean from two technical replicates, and two independent experiments gave similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. e Expression of the lumenal domain (LD) of C2 19K with a Flag tag, and a C-terminal ER retention signal (HDEL) is sufficient to induce XBP1s to levels similar as from the full-length 19K construct (left and middle panels). Immunofluorescence staining with the anti-19K 3A9 antibody in parallel samples depicts the expression levels of the full-length and the lumenal 19K proteins (right panel, scale bar, 50 µm). Data show a scatterplot of 20,000 randomly chosen cells per sample. Central line of the box plot indicates median with first and third quartiles, and whiskers are shown as boxes and lines, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.