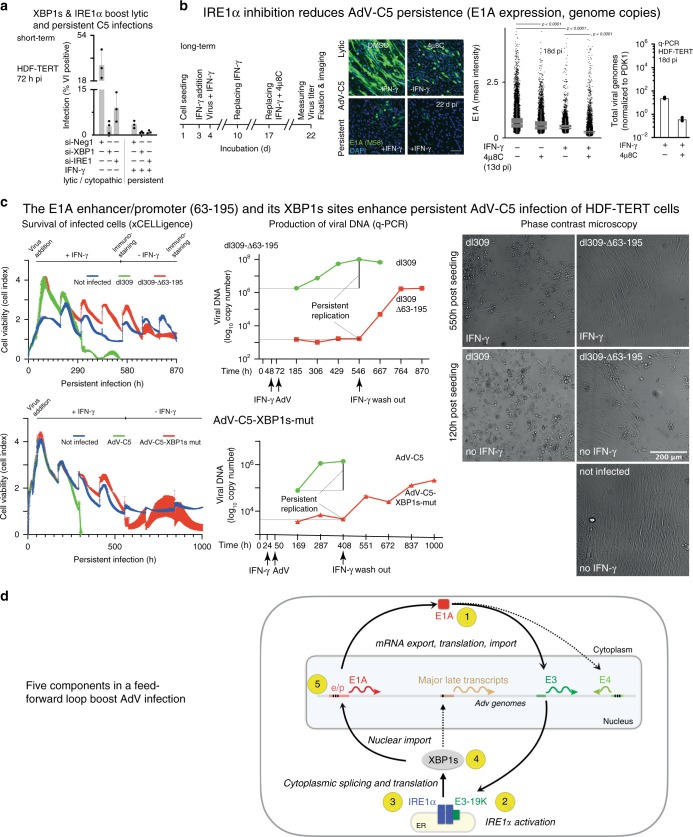
Fig. 7. IRE1α and XBP1s facilitate persistent and lytic AdV infections.
a Reduction in late AdV-C5 protein VI expression (MOI 180) of HDF-TERT cells upon RNA interference against IRE1α and XBP1 in the presence or absence of IFN-γ, including nontargeting siRNA (siNeg1). Data show the means ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). b E1A expression of AdV-C5-infected HDF-TERT cells (MOI 200, 37 °C, 1 h) with or without 500 IU IFN-γ, or IRE1α RNase inhibitor 4µ8C (100 µM) at 13 days pi was analyzed by immunofluorescence showing representative images (left) and a scatterplot with 15,000 cells per condition (middle). Data show the median, first and third quartiles, and whiskers as boxes and lines, respectively. Significance was assessed with two-tailed Wilcoxon nonparametric test (middle panels). Virus titers (q-PCR, right panel) were determined after 5 days of incubation with the drug (18 d pi). Q-PCR data show the means from two technical replicates. Two independent experiments gave similar results. Scale bar, 100 µm. c xCELLigence impedance plots showing HDF-TERT cell viability upon dl309 or dl309-63/195 and AdV-C5 or AdV-C5-XBP1s-mut infections (MOI 200). Cells were seeded on xCELLigence E-16 plate, and impedance readout for cell viability was measured live at 15-min intervals. Data show the means ± SD from three technical replicates. Two independent experiments gave similar results (left row). Experimental conditions and virus amount were as in panel b Genome copy numbers of virions released to the supernatant from the same experiment. Data show the means from two technical replicates. Two independent experiments gave similar results (middle row). Representative phase-contrast images of parallel samples imaged live for dl309 or dl309-63/195 infections (images on the right side, scale bar, 200 µm). d Schematic model depicting AdV infection under the control of a five-component feedforward loop. (1) The immediate early E1A protein transactivates early promoters. including the E3 and E4, giving rise to the 19K glycoprotein (2). Activation of IRE1α by 19 K increases XBP1s mRNA, and XBP1s protein (3), which translocates into the nucleus, and binds to the E1A enhancer/promoter (e/p) of the episomal viral genome (4). Binding of XBP1s to the E1A-e/p increases the E1A levels (5), which enhances output from the E3 promoter, enhances the 19K levels, and maintains a feedforward loop supporting viral persistence and lytic infection.