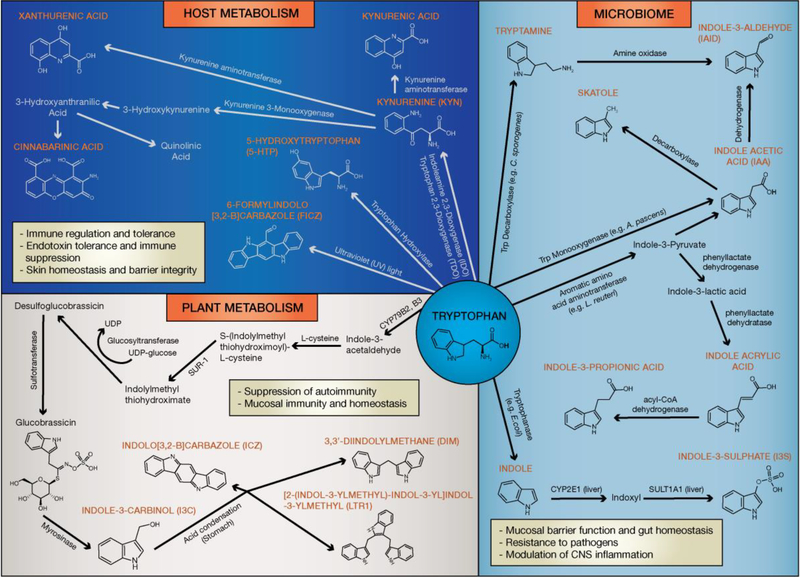
Figure 2: Biosynthesis of AhR ligands through the tryptophan metabolism.
Tryptophan is metabolized into a variety of AhR ligands affecting immunity, maintenance of epithelial barrier function and microbiome diversity. Host metabolites with AhR agonistic activity are primarily derived from tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenine pathway, with additional ligands produced by UV-exposure and oxidative reactions. In the GI tract multiple bacterial species (e.g. C. sporogenes, L. reuteri, E.coli, A. pascens) present in the microbiota metabolize tryptophan to products with potent AhR agonistic properties. Moreover, cruciferous vegetables contain the tryptophan metabolite glucosinolate, which undergoes a hydrolysis reaction forming the AhR protoagonist I3C. In the stomach I3C is metabolized via an acid-condensation reaction into the AhR ligands DIM, ICZ, and LTr1.