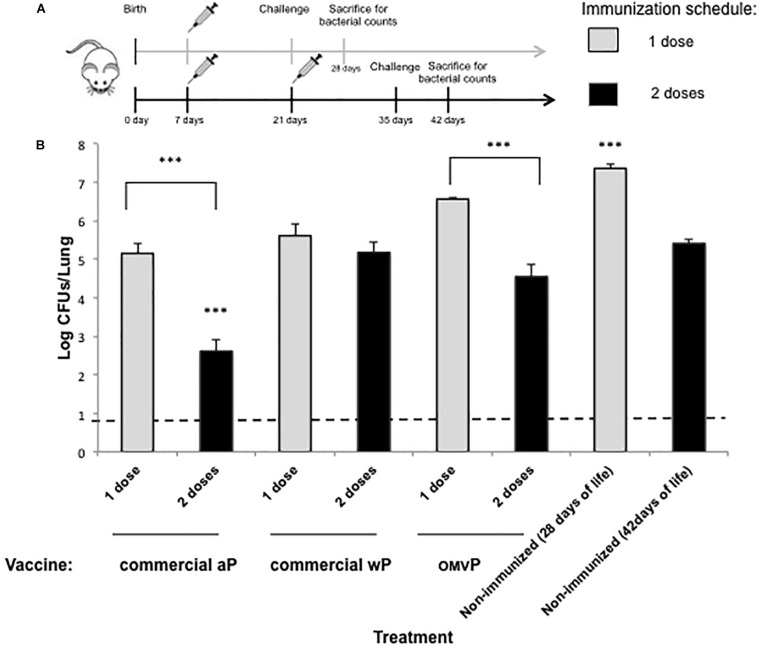
FIGURE 1.
Effect of neonatal immunization on the protection of offspring against Bordetella pertussis infection. (A) Schematic representation of vaccination and challenge protocols. Seven-day-old neonatal mice were vaccinated with a commercial aP, OMVP or a commercial wP vaccines (n = 8 in each group). For the two-dose vaccination schedules consisting in two doses, the second dose (black horizontal arrow) was administered 14 days after the first dose. Mice immunized with 1 dose (gray horizontal arrow) or 2 doses (black arrow) were challenged with B. pertussis at 28 and 35 days after birth, respectively. Non-immunized mice of the same age (used as a negative control for protection) were also challenged with B. pertussis. (B) Protection of offspring through the vaccination schedules of (A). The number of bacteria recovered from the mouse lungs, expressed as the log10(CFUs per lung), is plotted on the ordinate for the type and vaccine schedule indicated on the abscissa, with the data representing the means ± the SD. The dotted horizontal line demarcates the lower limit of detection. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 for both the non-immunized mice versus the 1-dose–immunized mice and the aP-immunized mice versus all the other treatments performed for the 2-dose–schedule assays.