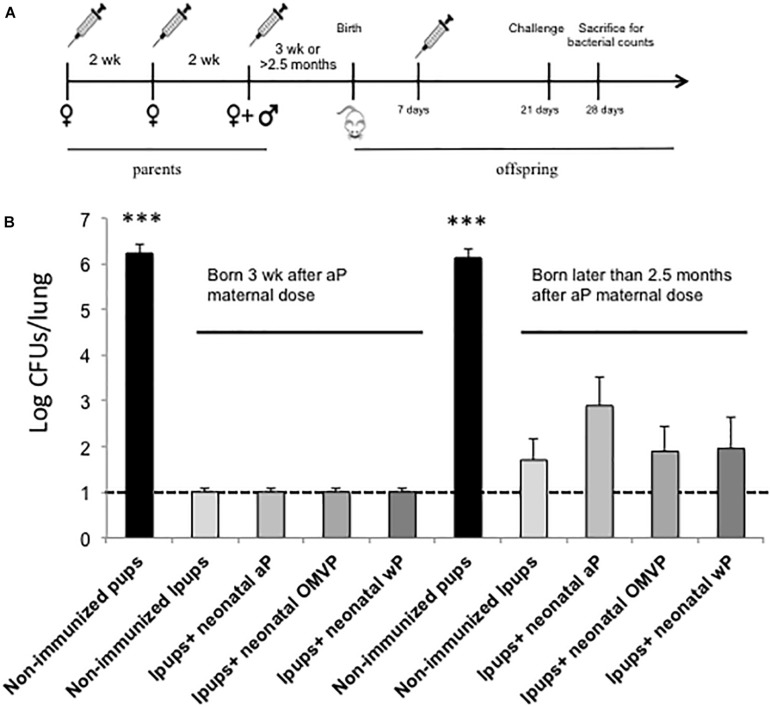
FIGURE 5.
Effect of neonatal immunization on the protection of pups with maternal immunity against B. pertussis infection. (A) Schematic representation of the vaccination and challenge protocols. Seven-day-old neonatal mice born either 3 weeks or later than 2.5 months after maternal aP immunization were vaccinated with a commercial aP or wP or the OMVP vaccine (n = 6 in each group). Non-immunized mice were used as a negative control for protection. All the groups were challenged with B. pertussis at 28 days after birth. (B) Protection of offspring through the vaccination schedules of (A). The number of bacteria recovered from the mouse lungs, expressed as the log10 of the CFUs per lung, is plotted on the ordinate for the treatments indicated on the abscissa, with the data representing the means ± the SD. The dotted horizontal line indicates the lower limit of detection. The left side of the panel depicts the CFU values for the different groups of mice born 3 weeks after the last maternal vaccination, while the right side contains the corresponding data for the same experimental groups born 2.5 months after that last maternal vaccination. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 non-immunized mice versus immunized Ipups. A significant difference (p < 0.05) was also recorded between the CFU values detected in the aP-vaccinated Ipups born 2.5 months after maternal immunization and those values detected in the non-vaccinated and vaccinated Ipups born 3 weeks after the completion of maternal immunization.