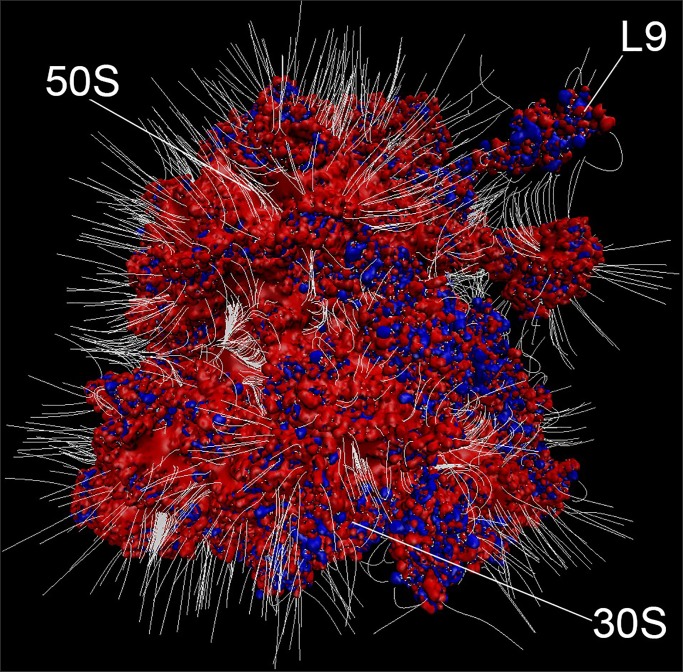
Fig 4. Electrostatic surface of the ribosome.
Electrostatic surface of the ribosome shows extensive negative potential consistent with the postulated function as an electrostatic sponge. Positive (blue, with potential > 10 kT/e) and negative (red, with potential < -10 kT/e) electrostatic isosurfaces of protonated E. coli ribosome (PDB code 4YBB [35]) were calculated by using Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver–Protein Data Bank to Protein Charge Radius, APBS-PDB2PQR, software. [36] White lines represent electric field lines at the surface of the ribosome imbedded in 0.3 M KCl. Electric field lines are calculated by using Visual Molecular Dynamics, VMD, software [37] with an magnitude gradient of 5 kT/(eÅ) and a maximum length of 29 Å, where k, T and e are the Boltzmann constant, temperature in Kelvin and electron charge, respectively. Ribosome subunits, 30S and 50S, as well as ribosomal protein L9 are indicated. The figure was rendered by using VMD.