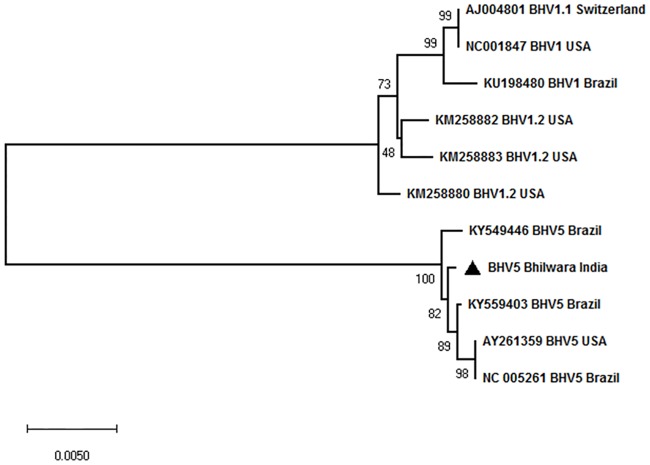
Fig 3. Phylogenetic analysis.
Nucleotide sequences from UL27, UL44 and UL54 genes (BoHV5//India/2018) were edited to 447, 1368 and 585 bp fragments respectively, using BioEdit version 7.0. These sequences, together with the representative nucleotide sequences of BoHV1 and BoHV5 available in the public domain (GenBank) were subjected for multiple sequence alignments. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted using MEGA X. To evaluate the evolutionary history of the strain as well as the phylogenetic relationship with different lineages, a concatemeric Neighbour-Joining method tree was generated. Test of phylogeny was performed using Maximum Composite Likelihood method and the confidence intervals were estimated by a bootstrap algorithm applying 1,000 iterations. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree.