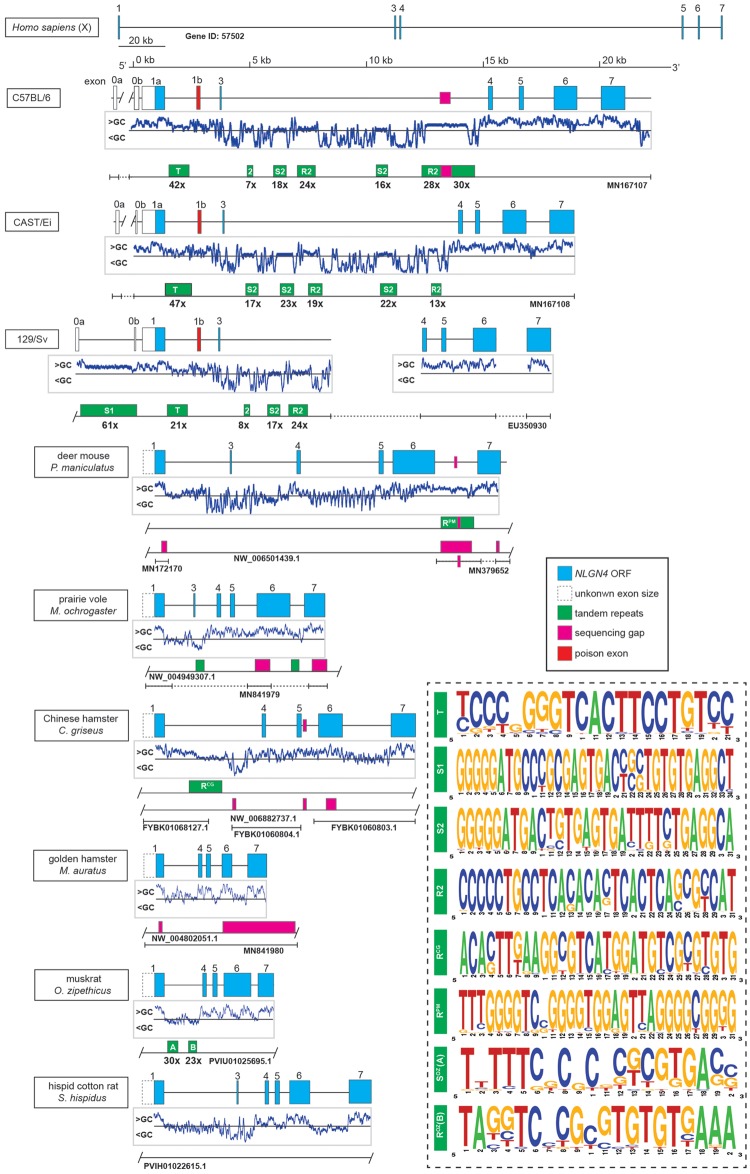
Fig. 2.
Organization of the neuroligin-4 gene in different mouse strains and hamster species. Schematic overview of the Nlgn4 gene in three mouse strains (C57BL/6J, MN167107; CAST/EiJ, MN167108; 129/Sv, EU350930), six hamster species (see supplementary data sheet 2, Supplementary Material online) and the human NLGN4X gene. The genes are drawn to scale with the exception of human NLGN4X. Neuroligin-4 coding regions are depicted in blue, open boxes represent upstream exon/s encoding the 5′-UTRs (in laboratory strains), partially dashed boxes (in hamster species) represent undetermined exon 1 sizes due to yet unspecified splice acceptor sites. Below, the mouse and hamster genes profiles of the relative GC contents are depicted indicating relatively high GC content (GC>50%) primarily in and around all exons. Additionally, initial sequencing gaps (magenta) from public sequence sources as well as repeat clusters (green) are placed on a separate bar. Bars with T-shaped ends indicate that beyond this point no sequence information is available, whether from public sources or our own sequencing efforts for a given stretch of DNA. Bar ends with a slash indicate that the given DNA information from a public source is only partially displayed. As not all repeat stretches are consistent in nature, only tandem repeats are displayed with their repeat numbers (for a general analyses of all repeats, nonmotif, or tandem, cf. supplementary data sheet 1, Supplementary Material online). The consensus motif of different tandem repeats is presented as a weblogo in the accompanying dashed box indicating the relative frequency of each base. The identity and relative position of the repeats in all lab mouse strains were comparable, only the repeat count varied. All mouse repeats were calculated using information from C57BL/6J, except for the repeat S1, which was calculated from the 129/Sv sequence deposited previously (Bolliger et al. 2008). An overview of the sequence sources can be found in the supplementary text file 3, Supplementary Material online.