Fig. 4. In vivo applications of smart contact lens systems.
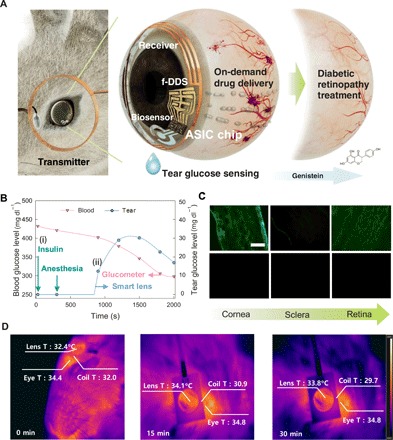
(A) Schematic illustration for in vivo diabetic diagnosis and therapy of the smart contact lens. (B) In vivo real-time wireless measurement of tear glucose levels with the smart contact lens. The blood and tear glucose levels were measured (i) after injection of insulin and anesthesia for wearing the smart contact lens in PBS. (ii) The tear glucose level increased due to the glucose in tears and decreased, reflecting the blood glucose level decrease due to the injected insulin. The blood glucose level was measured every 5 min with a commercial glucometer. (C) Fluorescence microscopic images of drugs absorbed in cornea, sclera, and retina of rabbits wearing the smart contact lens loaded with (top row) and without (bottom row) genistein. Scale bar, 0.1 mm. (D) Infrared thermal camera analysis for the temperature of the eye, smart contact lens, and transmitting coil after operating for 0, 15, and 30 min.
