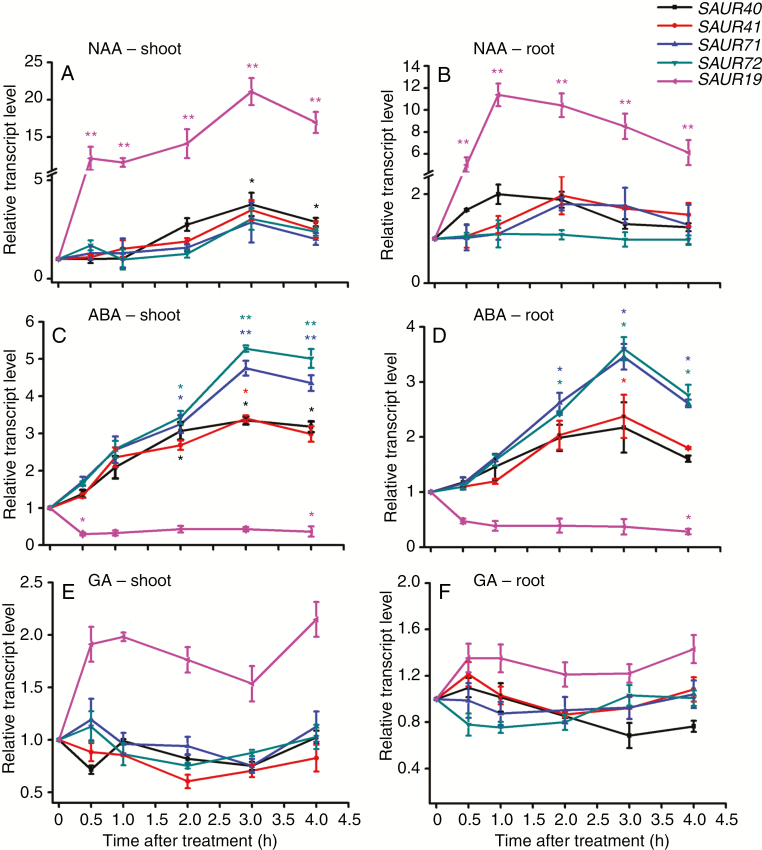
Fig. 2.
The SAUR41 subfamily genes are induced by ABA treatment. (A) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to NAA treatment in seedling shoots. Five-day-old seedlings were incubated in liquid medium containing 10 μm NAA for 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 h. SAUR19 seems dramatically auxin responsive. (B) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to NAA treatment in roots. (C) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to ABA treatment in seedling shoots. Five-day-old seedlings were incubated in liquid medium containing 10 μm ABA for 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 h. SAUR19 is repressed by ABA, unlike SAUR41 genes. (D) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to ABA treatment in roots. Again, SAUR41 genes are induced by ABA but SAUR19 is repressed by ABA. (E) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to GA treatment in seedling shoots. Five-day-old seedlings were incubated in liquid medium containing 10 μm GA for 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 h. SAUR19 is slightly induced by GA while SAUR41 genes are not induced by GA. (F) Transcriptional responses of SAUR41 genes and SAUR19 to GA treatment in seedling roots. Each treatment contained three biological replicates. In all cases, the transcript levels of each gene without hormone treatment were set to 1.0. Error bars represent the s.d. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test.