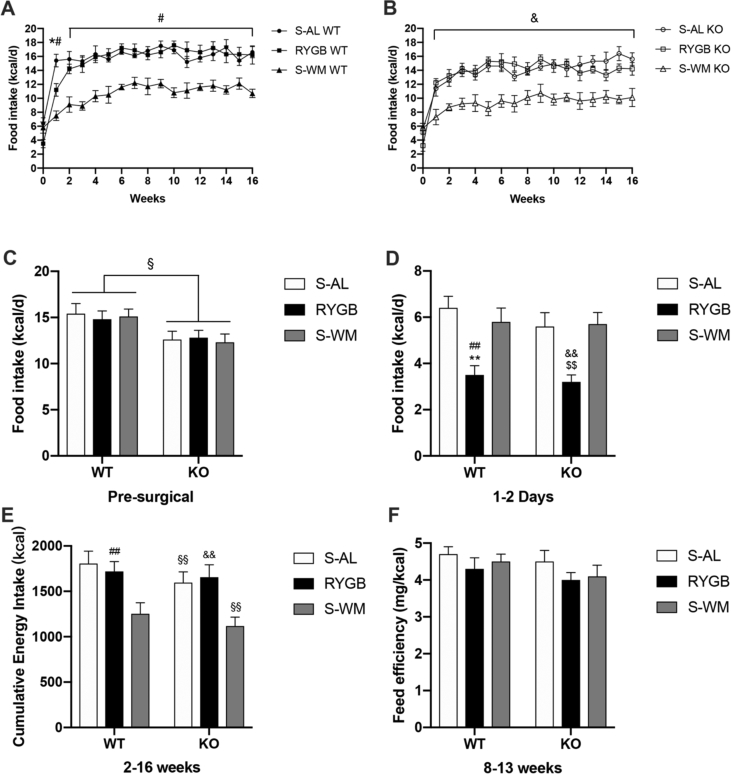
Figure 2.
Effect of RYGB, S-AL, or S-WM on food intake and feed efficiency in FXR−/− (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. (A) Food intake in WT mice. (B) Food intake in KO mice. (C) Presurgical food intake. (D) Ensure intake during the first 2 days. (E) Cumulative energy intake between 2 and 16 weeks. (D) Feed efficiency between 8 and 13 weeks in both WT and KO mice. ∗ = P < 0.05, ∗∗ = P < 0.01 S-AL vs. RYGB in WT mice, # = P < 0.05, ## = P < 0.01 S-WM vs. RYGB in WT mice, § = P < 0.05, §§ = P < 0.01 genotype comparison of mice with the same treatment conditions, $ = P < 0.05, $$ = P < 0.01 S-AL vs. RYGB in KO mice, & = P < 0.05, && = P < 0.01 S-WM vs. RYGB in KO mice by two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 8–10 per group). S-AL: sham-operated animals fed ad libitum; S-WM: sham-operated animals weight matched to RYGB-operated mice; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery; KO, knockout; WT, wild type.