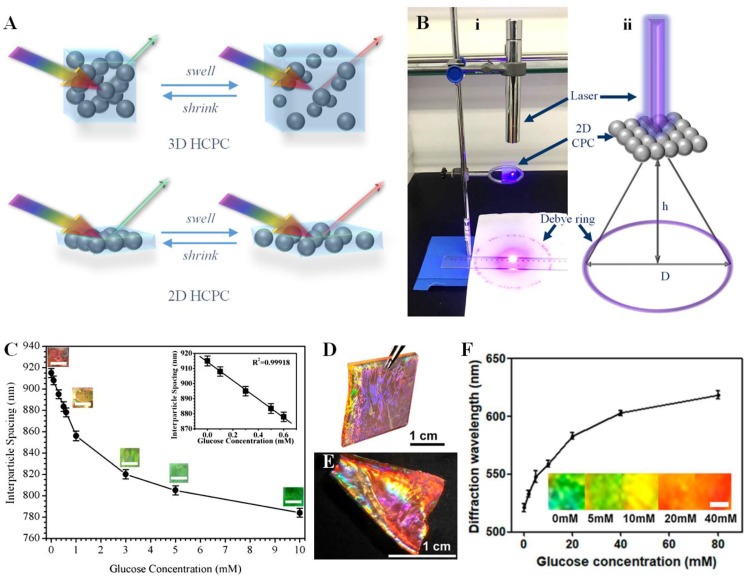
Figure 5.
(A) Comparison between 3D and 2D HCPCs: 3D HCPCs are formed by cross-linking hydrogel networks around a 3D colloid array, whereas 2D HCPC-sensing devices are formed by attaching a 2D CPC onto a hydrogel containing functionalized recognition groups. (B) Debye diffraction ring characterization: (i) the photograph shows the Debye diffraction ring resulting from a 2D CPC under 445 nm wavelength laser light, and (ii) a schematic diagram of Debye diffraction ring detection [74]. (C) Interparticle spacing change of a 2D HCPC with different glucose concentrations; the photographs show that the forward-diffraction color changed from red, through yellow, to green, and the inset shows a linear stop-band shifting with the increasing glucose concentration (0.1−0.6 mM) [80]. Photographs of (D) 2D Au CPC and (E) 2D Au HCPC that showed high diffraction efficiency. (F) Glucose concentration dependence of the diffraction wavelength of the 2D Au APBA -PAM-PVA HCPC device; inset shows photographs of the 2D HCPC film at different glucose concentrations [81].