Fig. 2.
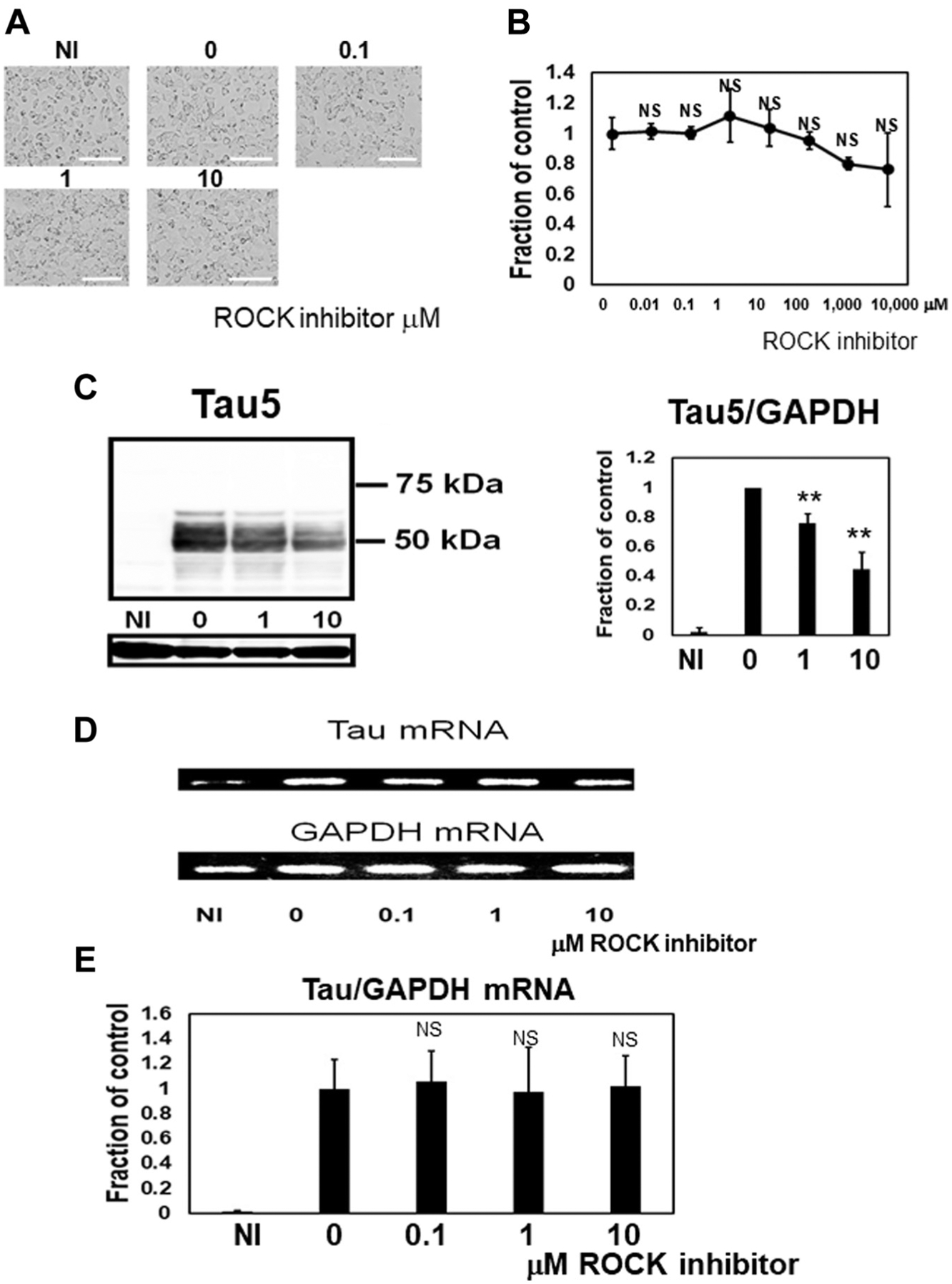
Western blot analysis showed reduced total tau levels by the ROCK inhibitor (H1152). The ROCK inhibitor (H1152) does not have cytotoxic effects. (A) ROCK inhibitor did not cause morphological change. Scale 25 μm. (B) No cell death under these conditions was observed in the ATP assay (0.01 μM-100 μM). N = 4, Data: ± SD. (C) To examine the effect of ROCK inhibitor on tau, M1C cells were induced to express tau for 5 d and exposed to ROCK inhibitor (1 or 10 μM) during the final day of the induction period. Lysates from cultures were analyzed by Western blot using the Tau5 antibody. These samples were probed with anti-GAPDH to confirm that loading among lanes was equal. Total tau levels decreased dose dependently after ROCK inhibitor treatment. In cultures treated with 1 μM ROCK inhibitor, the antibody Tau5 detected 45–60 kDa bands at 76.0% of the levels exhibited by the vehicle control. NI: noninduced cells, 0: untreated cells, 1: 1 μM ROCK inhibitor (H1152)-treated cells, 10: 10 μM ROCK inhibitor-treated cells. N = 6, **p < 0.01, Bar: ± SD. Tau mRNA was not affected by ROCK inhibitor treatment according to real-time PCR (D) and quantitative PCR (qPCR). N = 4, Bar: ± SD (E). Data from Tau5/GAPDH and Tau QPCR/GAPDH qPCR followed a normal distribution and were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, whereas the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was used for ATP assay because the data deviated from a normal distribution. Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NS, not significant; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase.
