Fig. 3.
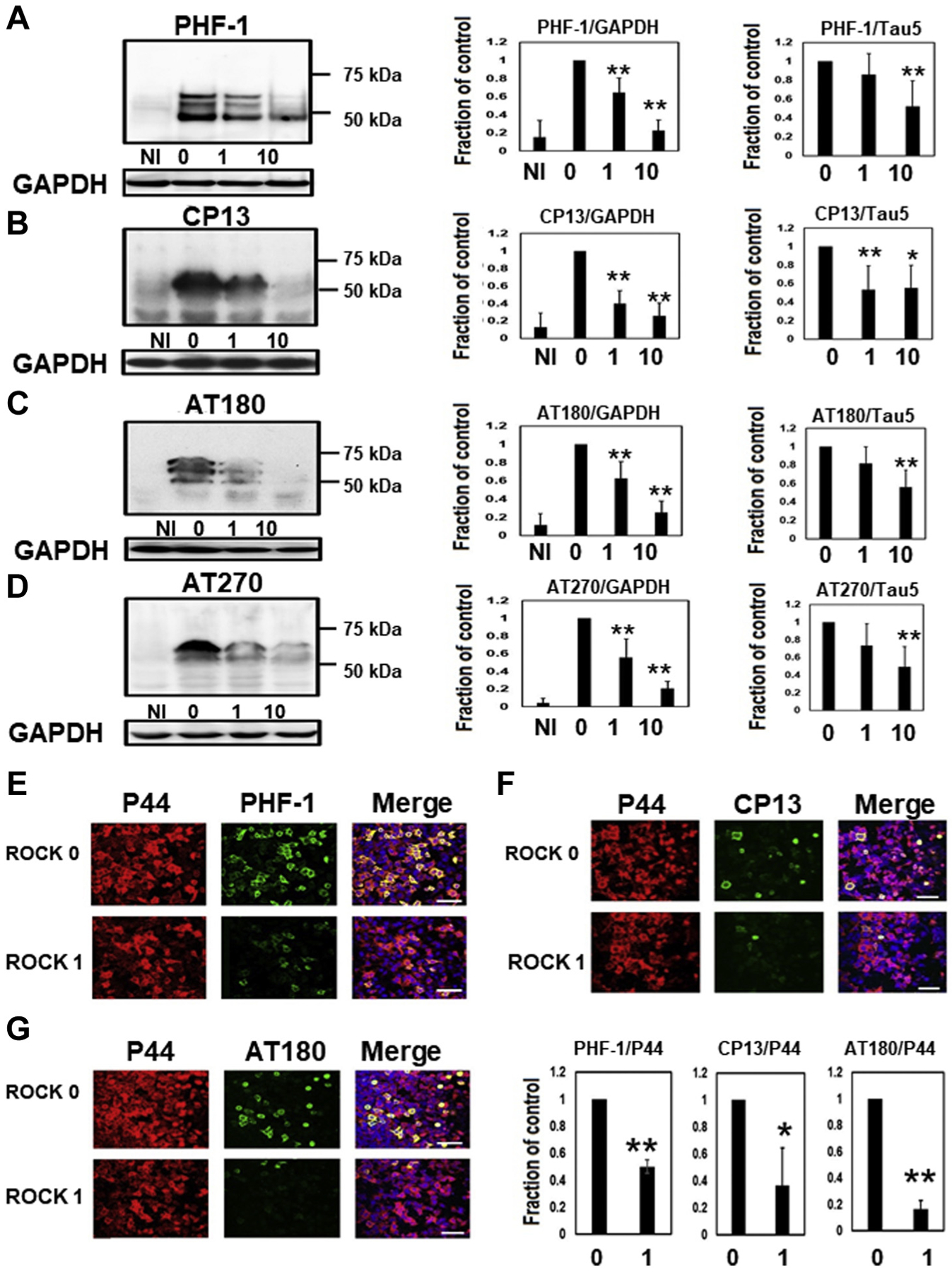
Phosphorylated tau levels were reduced in M1C cells by the ROCK inhibitor. Western blot analysis revealed reduced phosphorylated tau levels based on PHF-1 (A), CP13 (B), AT180 (C), and AT270 (D) by ROCK inhibitor (H1152). N = 5, **p < 0.01, *<0.05, Bar: ± SD. NI: noninduced cells, 0: untreated cells, 1: 1 μM ROCK inhibitor-treated cells, 10: 10 μM ROCK inhibitor treated cells. According to the immunocytochemical study, PHF-1(E), CP13 (F), and AT180 (G)-positive phosphorylated tau was markedly reduced by the ROCK inhibitor (H1152) (0): 0 μM ROCK inhibitor, (1): 1 μM ROCK inhibitor. N = 5, **p < 0.01, *<0.05, Bar: ± SD, Scale 75 μM. Data from PHF-1/GAPDH, CP13/GAPDH, AT180/GAPDH, AT270/GAPDH, PHF-1/Tau5, AT180/Tau5, and AT270/Tau5 followed a normal distribution and were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, whereas the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was used for CP13/Tau5 because the data deviated from a normal distribution. For the immunocytochemical study of PHF-1/P44, CP13/P44, and AT180/P44, the data followed a normal distribution and were analyzed with Student’s t-test. Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase.
