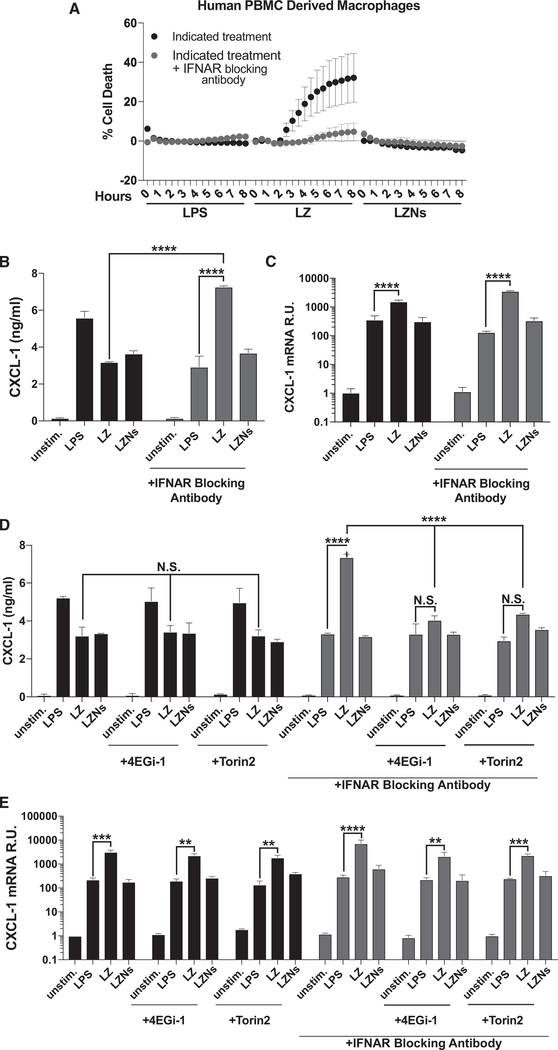
Figure 6. IFN Signaling Regulates RIPK-Dependent Cytokine Translation in Human PBMCs.
(A) Cell death as measured by propidium iodide incorporation over 8 h in human PBMC-derived macrophages stimulated as indicated ± overnight treatment with IFNAR-blocking antibody.
(B and C) CXCL-1 protein (B) and mRNA (C) levels in human PBMC-derived macrophages stimulated as indicated ± overnight treatment with IFNAR-blocking antibody
(D and E) CXCL-1 protein (D) and mRNA (E) levels in human PBMC-derived macrophages stimulated as indicated ± overnight treatment with IFNAR-blocking antibody and/or treatment with 4EGi-1 or Torin 2.
In all panels, human PBMC-derived macrophages were stimulated with LPS, LZ, or LZNs as indicated. ELISA and qPCR data are shown as ±SD from three independent experiments compared using two-way ANOVA: n.s. (p > 0.05), **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Kinetic cell death experiments are representative of three or more independent experiments and presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate wells.