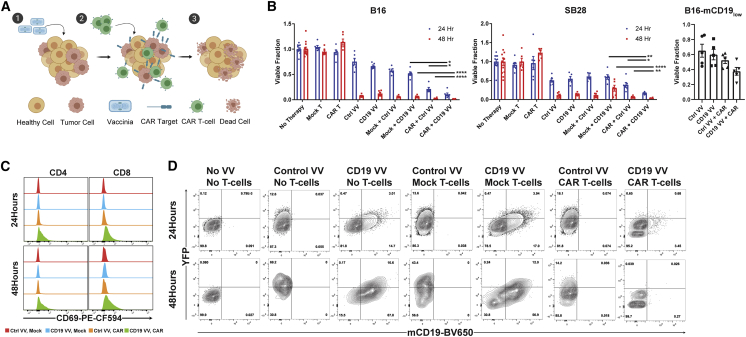
Figure 3.
mCD19 CAR T Cells Eliminate mCD19 VV-Infected Tumor Cells In Vitro
(A) Schematic of tumor-selective delivery of CAR targets by an oncolytic VV followed by selective clearance by antigen-matched CAR T cells. (B) In vitro co-culture studies with B16 (left) and SB28 (middle) highlight the greatest combinatorial toxicity with co-culture of mCD19 CAR T cells and tumor cells infected with mCD19 VV. Mock + CD19 VV versus CAR + CD19 VV: p < 0.0001, t = 9.413, df = 10 (B16, 24 h); p = 0.0009; t = 4.654, df = 10 (B16, 48 h); p < 0.0001, t = 6.993, df = 10 (SB28, 24 h); p = 0.0073, t = 3.356, df = 10 (SB28 48 h). CAR + Ctrl VV versus CAR + CD19 VV: p = 0.0272, t = 2.584, df = 10 (B16, 24 h); p = 0.0337, t = 2.459, df = 10 (B16, 48 h); p = 0.0076, t = 3.332, df = 10 (SB28, 24 h); p = 0.0377, t = 2.395, df = 10 (SB28, 48 h). n = 6 independent cultures for each combination, time point, and cell line. CAR T cell efficacy at 24 h of co-culture benefits from VV-induced augmentation in levels of mCD19 in a B16-mCD19 cell line that expresses low levels of mCD19 (right). CAR + Ctrl VV versus CAR + CD19 VV: n = 5 independent cultures for each combination, p = 0.0618, t = 2.170, df = 8. (C) Expression of the early activation marker CD69 is upregulated in the antigen-matched combination of mCD19 VV-infected B16 cells and mCD19 CAR T cells in in vitro co-culture. (D) The presence of CAR T cells eliminates all mCD19+ cells by 48 h of co-culture with mCD19 VV-infected B16 cells. Populations are shown gated on CD4−CD8− double-negative cells. All statistical analyses were performed with unpaired two-tailed t tests. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.