Fig. 8.
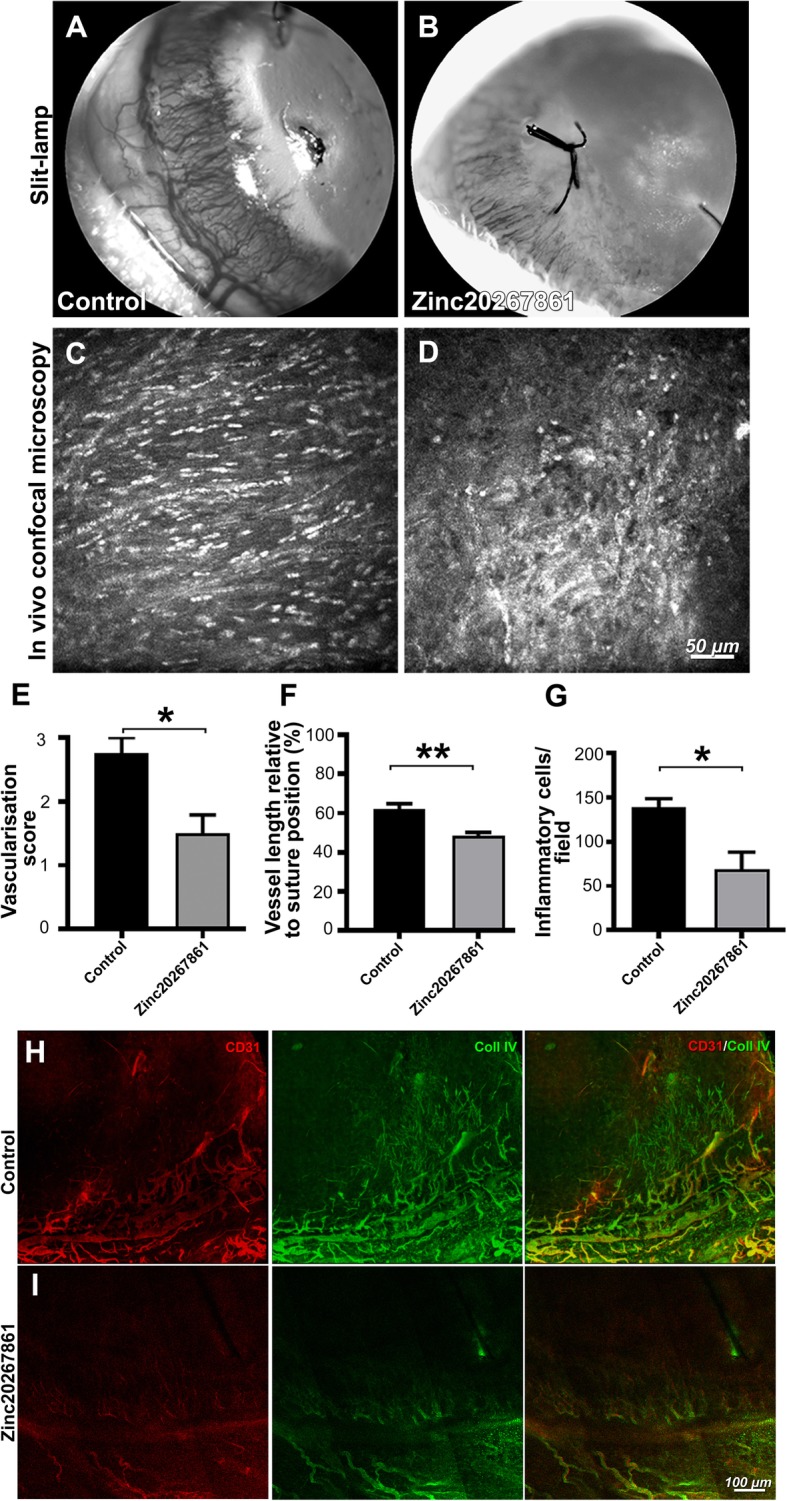
Evaluation of Zinc20267861 topical treatment in rat suture-induced corneal neovascularization model in vivo. Slit-lamp images of the neovascularization of sutured rat corneas at 96-h time point, treated either with vehicle (10% DMSO in 50% PBS/water) (a) or Zinc20267861 (5 μg/μl; 10.3 μM in 10% DMSO in 50% PBS/water) (b). In vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) images depicting corneal stromal inflammatory cell infiltration in vehicle-treated controls (c) and Zinc20267861 5 μg/μl topical treatment (d). Semi-quantitative vascular density and vascular progression score (e). Quantification of neovessels length % relative to suture position (f). Quantification of infiltrating inflamatory cells per 400 × 400 μm area (g). Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 and Coll IV in rat corneal whole mounts 96 h after induction of SI-CNV, treated topically either with vehicle (h) or Zinc20267861 (i). CD31/Coll IV double-positive signals visualize mature perfused vasculature with developed endothelia. Immature basement membranes are visualized by Coll IV signal only. Student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance in all three quantitative analysis of in vivo data. *p < 0.05; (n = 4)
