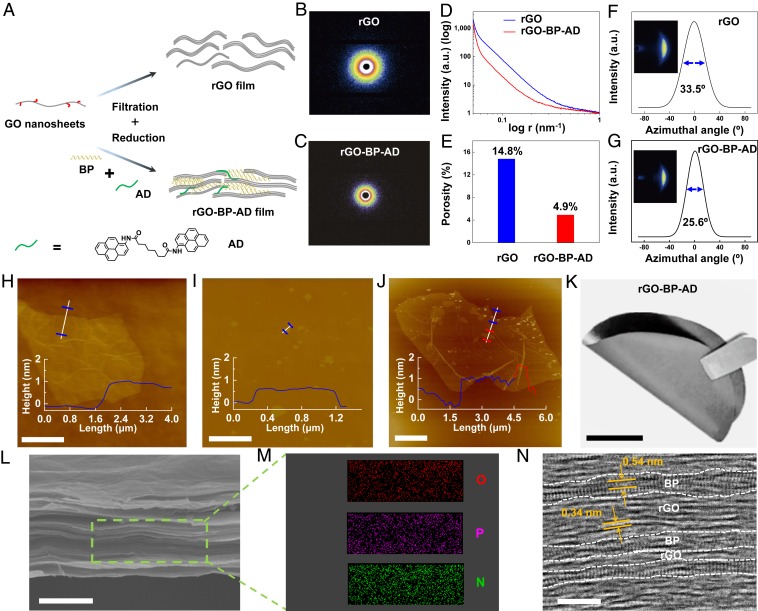
Fig. 1.
Fabrication process of bioinspired rGO-BP-AD films. (A) Illustration of the manufacturing process of BP functionalized graphene films. SAXS patterns of (B) pure rGO and (C) rGO-BP-AD films. (D) Corresponding intensity curves according to the SAXS patterns. (E) Porosity of the pure rGO and rGO-BP-AD films. The WAXS patterns of (F) rGO and (G) rGO-BP-AD. AFM of (H) monolayer GO nanosheets, (I) BP nanosheets, and (J) covalently cross-linked GO-BP nanosheets. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (K) A digital photograph of rGO-BP-AD. (Scale bar, 2 cm.) (L) SEM of cross-sectional view of rGO-BP-AD films. (Scale bar, 2 μm.) (M) EDS mapping of O, P, and N elements. (N) HR-TEM image of the cross-section of the bioinspired rGO-BP-AD films, which shows three to six layers of monolayer BP nanosheets with the d-spacing of 0.54 nm and rGO nanosheets with the d-spacing of 0.34 nm. (Scale bar, 5 nm.)