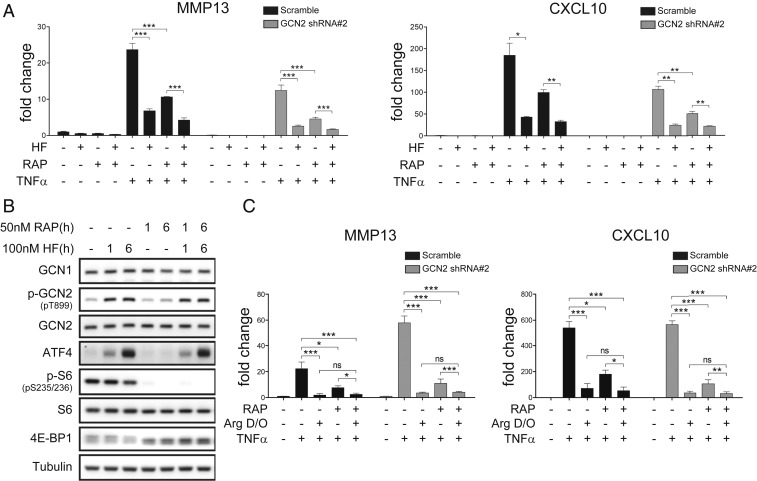
Fig. 3.
HF and amino acid limitation each inhibit inflammatory responses in the absence of mTORC1 signaling. (A) HF inhibits TNF-α induction of MMP13 in the absence of detectable mTORC1 pathway activity. Wild-type or shRNA GCN2-depleted K4 fibroblasts were pretreated with 100 nM HF for 16 h, and then treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 6 h. Transcript levels of target genes (MMP13, CXCL10) were quantified by qPCR. (B) Effects of HF and rapamycin on AAR (p-GCN2, ATF4) and mTORC1 (p-S6, 4E-BP1) pathway activation. (C) Arginine deprivation inhibits TNF-α induction of MMP13 or CXCL10 in the absence of detectable mTORC1 signaling, in both wild-type and GCN2 KD K4 cells. Wild-type or shRNA GCN2 depleted K4 fibroblasts were switched to arginine D/O DMEM for 16 h, and then treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 6 h. Results are representative of three independent experiments (means ± SD, n = 3), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.