Figure 6.
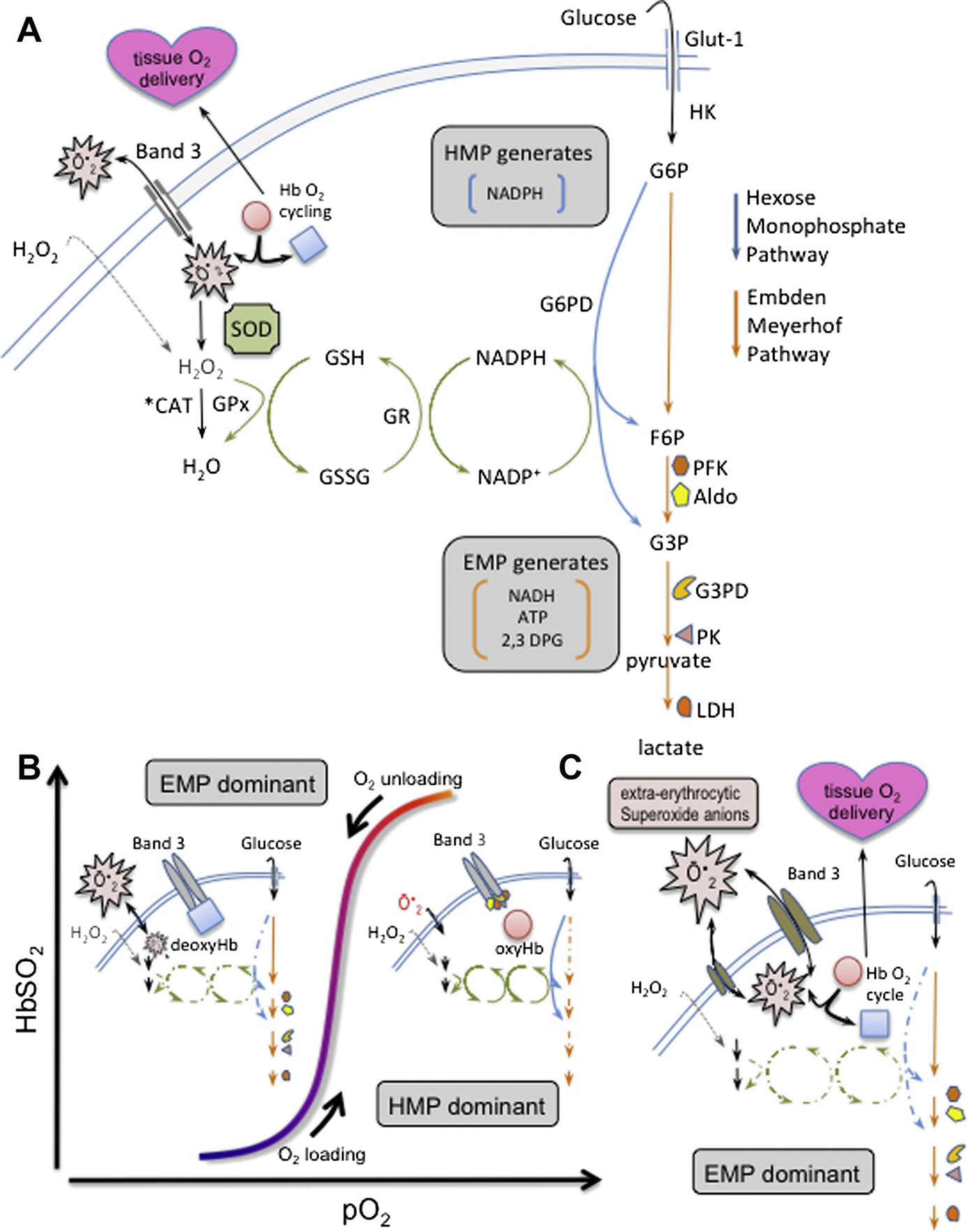
Simplified scheme of cdB3-based control of RBC metabolism and proposed causal path for sepsis induced red cell dysfunction: (A) Energy metabolism in RBCs proceeds through either the Embden-Meyerhof pathway (EMP, orange arrows), or the hexose monophosphate pathway (HMP, blue arrows, AKA ‘pentose shunt’). Both share glucose-6 phosphate (G6P) as initial substrate. The HMP is the sole source of NADPH in RBCs and generates fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), which rejoin the EMP prior to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PD/GAPDH), a key regulatory point. The EMP generates NADH (utilized by metHb reductase), as well as ATP (to drive ion pumps) and 2,3-DPG (to modulate hemoglobin P50). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion (O2−) are the principal endogenous reactive O2 species (ROS) that are generated / encountered by RBCs. Both ROS are generated internally in the course of HbO2 cycling.230–232 Notably, only H2O2 can cross the membrane directly. O2− enters/departs RBCs via the Band 3 channel (anion exchange protein 1, or AE-1). O2− and H2O2 are ultimately reduced to water by catalase (CAT) or glutathione peroxidase (GPx). (B) O2 content modulates EMP/HMP balance via reciprocal binding for cdB3 between deoxyHb and key EMP enzymes (PFK, Aldo, G3PD, PK, and LDH). In oxygenated RBCs (right half of stylized O2 dissociation plot), EMP enzyme sequestration to cdB3 inactivates this pathway, resulting in HMP dominance and maximal NADPH (and thus GSH) recycling capacity. In deoxygenated RBCs (left half of O2 dissociation plot), deoxyHb binding to cdB3 disperses bound EMP enzymes, activating the EMP, creating G6P substrate competition, constraining HMP flux, limiting NADPH and GSH recycling capacity and weakening resilience to ROS, such as O2−. (C) In sepsis, data suggest cdB3-complex assembly may be prevented (particularly, with coincident hypoxia, see text). As in settings similarly impacting the cdB3 complex, it appears that this disturbs normal EMP/HMP balance (disfavoring HMP), depowering antioxidant systems and rendering RBCs vulnerable to oxidant attack. GSH, glutathione; GR, glutathione reductase; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PFK, phosphofructokinase; Aldo, aldolase; PK, pyruvate kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase
