Fig. 1.
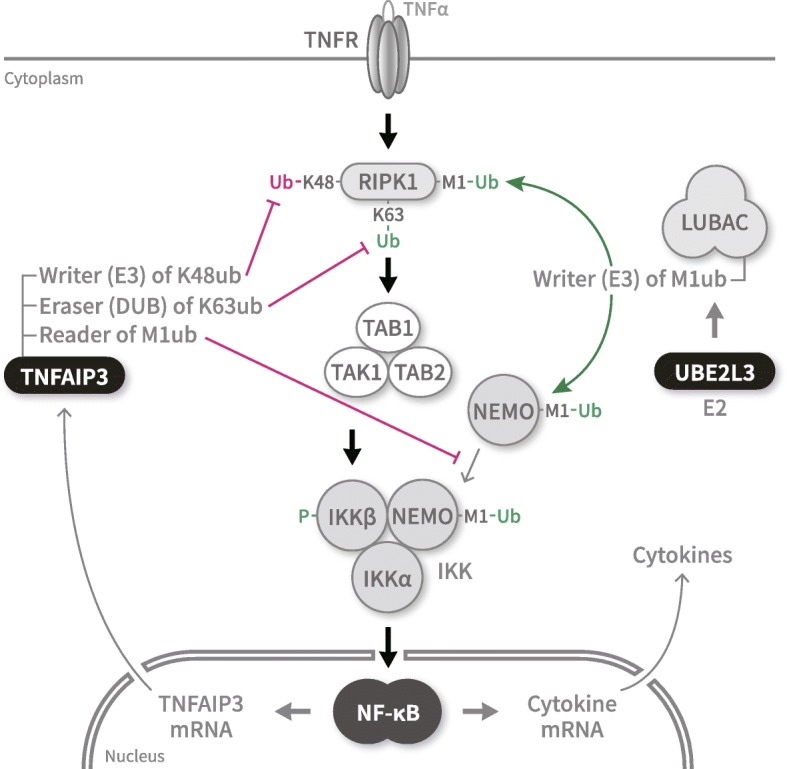
Participation of TNFAIP3 and UBE2L3 in regulation of NF-κB activity under TNFα signaling. The human TNFR pathway transduces a signal of extracellular TNFα through cytoplasmic IKK to latent transcription factor NF-κB for cytokine induction in the nucleus, among others. TNFAIP3 negatively regulates NF-κB (marked by red arrows) (1) by mediating RIPK1 degradation via K48 ubiquitylation (E3), (2) by inactivating RIPK1 via K63 deubiquitylation (DUB), and (3) by inhibiting IKK via binding ubiquitylated M1 of NEMO. In contrast, UBE2L3 (E2) positively regulates NF-κB (marked by green arrows) by helping LUBAC (E3) to activate RIPK1 and MEMO via M1 ubiquitylation
