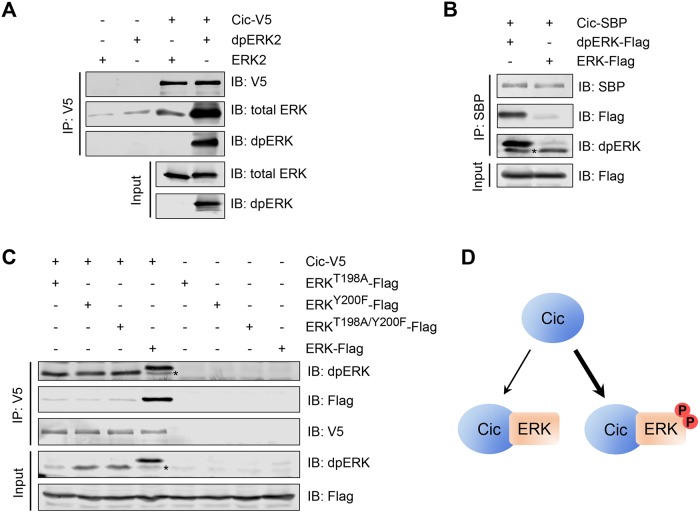
FIGURE 1:
ERK phosphorylation in the activation loop is required and sufficient to induce strong binding to Cic. (A) An in vitro binding assay in which bacterially expressed purified rat ERK2 and dpERK2 were incubated with beads bound with Cic-V5 purified from S2 cells, analyzed by Western blotting. Cic-V5 strongly prefers dpERK2 over unphosphorylated ERK2. (B) An in vitro binding assay in which protein lysates from S2 cells cotransfected with Drosophila ERK-Flag, Raf, and MEK (dpERK-Flag) or transfected only with ERK-Flag were incubated with beads bound with separately expressed Cic-SBP, analyzed by Western blotting. Cic-SBP strongly prefers dpERK over unphosphorylated ERK. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation between Cic and ERK mutants in Drosophila S2 cells, analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Blocking the formation of dually phosphorylated ERK (dpERK) results in a lower affinity for Cic. Asterisks in B and C indicate endogenous (untagged) dpERK present in S2 cells. (D) Summary of Cic interactions with ERK and dpERK. Cic preferentially associates with dpERK.