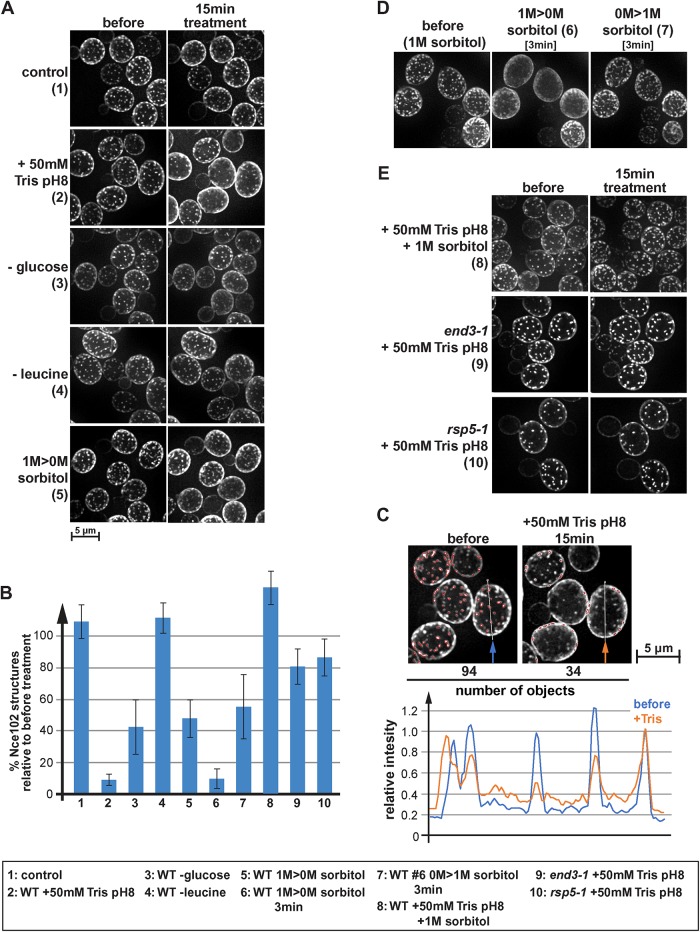
FIGURE 1:
Eisosomes respond differently to various stress conditions. (A) Wild type expressing Nce102-mCherry (AMY4) was monitored by fluorescence microscopy for changes in localization of Nce102. The pictures show the projection of 10 optical sections representing the bottom half of the cell. Cells were maintained in a microfluidics system under optimal growth conditions (SDcomp medium at 30°C) (1) and then shifted to different stress conditions for 15 min. To disrupt the proton gradient, 50 mM Tris buffer, pH 8, was added to conditioned growth medium (medium obtained by centrifugation of the starting culture, which is identical to the medium of the control cells), which changed the pH from 4 to 7.5 (2). For glucose and leucine starvation, SDcomp medium buffered to pH 4 was used lacking either glucose or leucine (3 and 4). For the hypoosmotic shock (1 M > 0 M sorbitol) (5), cells were grown in SDcomp + 1 M sorbitol and shifted to conditioned SDcomp lacking sorbitol (this medium was obtained from a parallel culture that grew to the same cell density in absence of sorbitol). (B) Quantification of eisosomes using a 2D-polygon analysis (see Materials and Methods). The error bars indicate the SD of four to five analyzed microscopy pictures containing on average ∼40 cells each. (C) Example of the 2D polygon analysis used to quantify changes in Nce102 localization (B). The microscopy pictures are identical to those shown in A2. Red outlines mark the by the algorithm identified objects. The line graph shows the intensity profile along the line indicated in the micrographs. The intensity profiles were standardized to the last peak (set to 1.0). (D) Wild-type cells expressing Nce102-mCherry (AMY4) were grown in SDcomp + 1 M sorbitol, shifted for 3 min to conditioned medium lacking sorbitol, and then shifted back for 3 min to conditioned medium containing 1 M sorbitol. (E) Wild-type, end3-1, and rsp5-1 cells expressing Nce102-mCherry (AMY4, DAY20, DAY21) grown in SDcomp were treated with 50 mM Tris buffer, pH 8, in conditioned medium either in the presence or in the absence of 1 M sorbitol.