Figure 7. Granisetron (GRS) restored Ca+2 homeostasis by modulating calcium pathway and significantly improved memory as determined by Morris Water Maze test in TgSwDI mice.
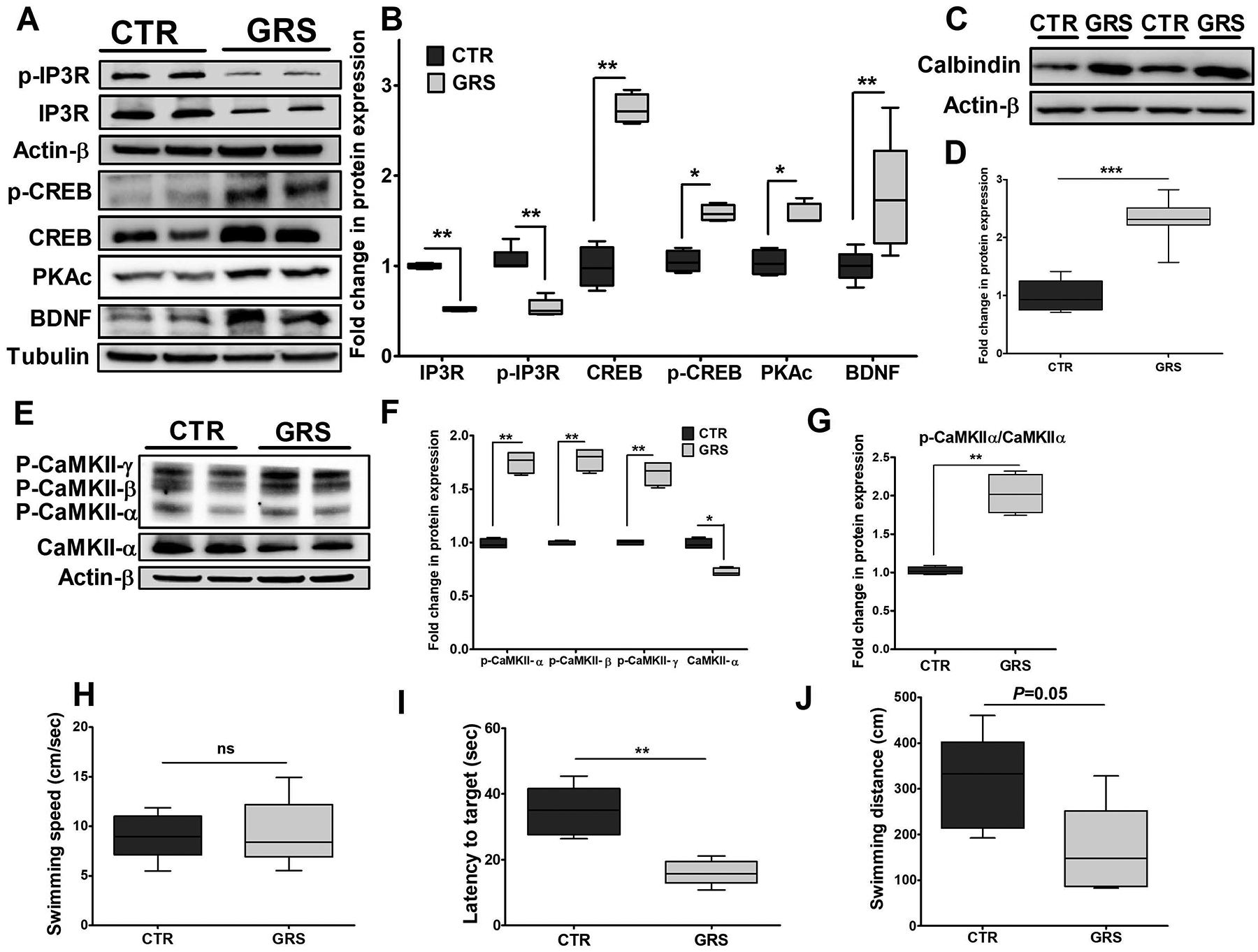
(A) Representative blots, and (B) densitometry analysis showed granisetron treatment significantly reduced total IP3R and p-IP3R expressions, and increased PKAc, BDNF, CREB and p-CREB expressions, which play major role in enhancing LTP. (C) Representative blots, and (D) densitometry analysis showed significant increase in the expression of the Ca+2 buffering protein calbindin D28K. (E, F, G) Representative blots and densitometry analysis showed significant reduction in CaMKII expression with increased levels of phosphorylated-CaMKII α, β, γ isoforms. Values were normalized to CTR (1.0). The effect of granisetron treatment on (H) swimming speed, (I) latency to target, and (J) swimming distance of the mice. Granisetron significantly decreased latency and swimming distance compared to the vehicle treated TgSwDI mice (control, CTR). Data are presented as box-and-whisker plots representing median and IQR, with minimum and maximum values. Statistical analysis was determined by Student’s t-test (n=5 mice per group). ns = not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 versus control group.
