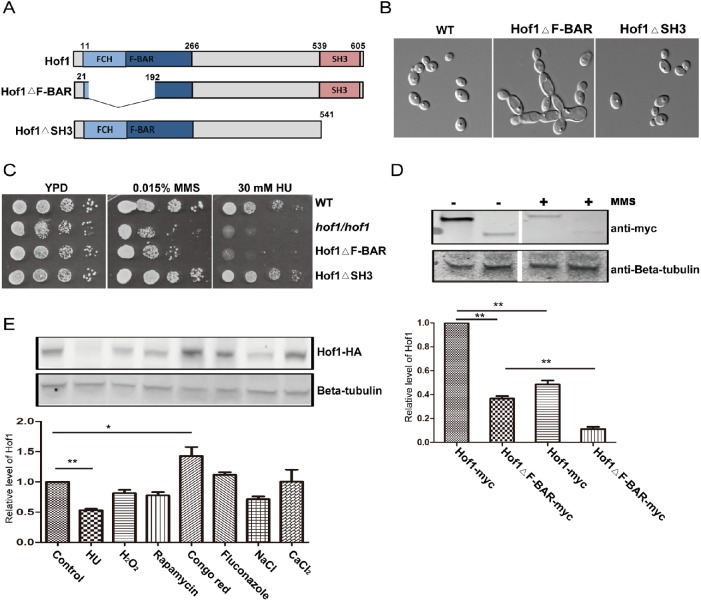
FIGURE 4:
Functional analysis of the Hof1 F-BAR and SH3 domains. (A) Schematics of C. albicans Hof1 and the Hof1ΔF-BAR and Hof1ΔSH3 mutants. (B) Cell morphologies of WT and Hof1 mutant strains grown in YPD imaged with DIC optics. (C) Growth assays of WT and Hof1 mutant strains in the presence of genotoxic stresses. (D) Western blot of samples from log phase Hof1-myc and Hof1ΔF-BAR-myc cultures showing expression levels in the absence and presence of MMS (0.02% for 90 min). b-Tubulin is a loading control, and normalized band intensities are shown below. (E) Expression of Hof1-HA tested by Western blotting after treating log phase cells with 40 mM HU, 2.5 mM H2O2, 10 nM rapamycin, 100 μg/ml Congo red, 5 μg/ml fluconzole, 1.5 M NaCl, or 200 mM CaCl2 for 90 min before lysis. Control cells were untreated and Hof1 was probed using an anti-HA antibody. b-Tubulin acts as a loading control and normalized band intensities are shown below. Two-tailed t test; n = 3; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.